Herpes Encephalitis
What is Herpes Encephalitis?
Herpes Encephalitis which is otherwise known as herpetic brainstem encephalitis, herpetic meningoencephalitis or HSE is a medical condition that, according to statistics, is responsible for the 10 percent of the persons who are suffering from encephalitis. Encephalitis is a medical condition that happens when there is an inflammation in the brain because of viral infections and other kinds of infections. Other would define herpes encephalitis as a viral kind of encephalitis. Meanwhile, herpes simplex virus (1) is a common blister that results to the person experiencing cold sores or small blisters in his or her nose, eyes, eyelid or lips. It can also progress and affect the brain portion of the person. It can lead to the severe kind of amnesic syndrome which results to the damage to the medical part of the temporal lobes.
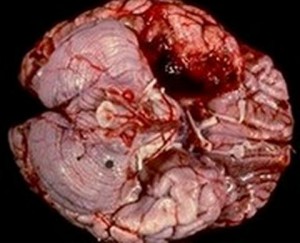
Fig 1 – Actual Picture of a Unilateral Temporal Lobe Necrosis as seen in Herpes encephalitis
The herpes simplex virus which is found in the herpes encephalitis can occur to anybody at any age and at anytime. According to statistics, United Kingdom has 200 cases of persons who suffer from herpes encephalitis. Yet, despite of the huge number recorded, this disease condition is sometimes under diagnosed.
Herpes Encephalitis Symptoms
In preventing the under diagnosis of herpes encephalitis, one must note the symptoms associated with herpes encephalitis. The symptoms that are present in persons suffering from herpes encephalitis can be variable to one person to another. The common symptoms are as follows:
- Memory loss
- Dysphasia
- Headache
- Fever
- Hyperactivity
- Seizure
- Vomiting
- Loss of visual field
- Altered consciousness
- Behavior changes
- Anorexia
- Swelling of the temporal lobe
- There is an increase protein in the person’s blood lymphocytes and cerebrospinal fluid
- One side muscle weakness
- Stiff neck
- General weakness
- Coma
- Poor feeding
- Stiffness of the body
Herpes Encephalitis Causes
Normally, according to research, herpes encephalitis can occur about 5 to 10 days or after the occurrence of childhood illness. Sometimes, the herpes encephalitis can occur in weeks, months, or even in years after the first viral infection occurs.
Persons that suffer from herpes encephalitis experiences the disease condition because of either:
- Herpes Simplex virus type I
- Herpes Simplex virus type II
Among the type of herpes simplex virus mentioned, usually persons that suffer from herpes encephalitis have herpes simplex virus type I. When a person has herpes simplex virus type I, they usually have the disease condition at the early stage of his or her life. Yet, they may not notice it for the person may have an asymptomatic infection or an infection that has no present symptoms.
The herpes encephalitis can be widespread yet it is rare in nature. The herpes encephalitis is an infection that enters the brain because of the following reasons:
- It enters the blood brain barrier
- It enters the central nervous system
- It enters via the nerves pathways that links the brain to other areas
Herpes Encephalitis Treatment
As mentioned earlier, herpes encephalitis is a brain inflammation that can also be medically referred to encephalitis. The herpes encephalitis is a viral infection that attacks the person’s neurons which leads to the hemorrhagic process especially in the inferior part of the medical temporal and frontal lobes of the person’s brain. Once, one is positive with herpes encephalitis, there is a need for special medical attention to prevent the deterioration of the person’s central nervous system and avoid any fatal complications associated with herpes encephalitis. The treatment for herpes encephalitis is symptomatic in approach. Hence, the treatment may also vary basing on the symptoms experienced by the person. The following are the treatment given and provided to persons who are suffering from herpes encephalitis:
Initial treatment
Initial treatment is given to persons who have herpes encephalitis. It includes the following treatment management:
- General nutritional support
- Fluid support
- Airway management
- Breathing management
- Circulation management
- Proper universal precaution is also given
- Monitoring of seizure and increase in intracranial pressure
Steroid treatment
Steroid treatment is given to persons who suffer from herpes encephalitis to suppress the response of the immune system which will limit the replication of the virus. Aside from that, it is reported to reduce the edema of the person’s brain especially in those persons who suffer from the severe form of the herpes encephalitis.
Antiviral treatment
This is the common treatment given to persons with herpes encephalitis. Under this drug category, you can find acyclovir which is a medical choice for the herpes encephalitis. The good thing about this drug is that it has lesser side effects which make it an ideal drug to persons suffering from herpes encephalitis. This is often given intravenously. It usually is given for a period of 14-21 days.
Herpes Encephalitis Prognosis
The prognosis for persons with herpes encephalitis will depend greatly on the viral infection or the agent which is involved, the treatment given, and the severity of the herpes encephalitis itself. Persons who have a mild form of herpes encephalitis usually achieve full recovery but the process towards recovery is slow. Generally, persons with herpes encephalitis needs long term medication, supportive care and therapy for them to recover fully.
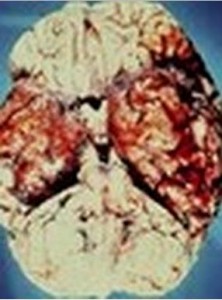
Fig 2 – A Severe Form of Herpes Encephalitis Affecting both the Temporal Lobes
Is Herpes Encephalitis Contagious?
Through direct contact, herpes encephalitis is rarely forwarded to persons who were never infected with herpes encephalitis. Those who have never been infected with herpes encephalitis are at high risk in acquiring herpes and recurrence of the sores in the future. Hence, a person with herpes simplex is needed to be given with contact precaution because they have the tendency to inflict other persons.