Osteogenesis Imperfecta
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Osteogenesis imperfect (OI) is a bone disorder involving genetic predisposition. It is also called as Lobstein syndrome or brittle bone disease. Individuals with osteogenesis imperfect lacks Type-1 collagen, which leads to defects in the connective tissue or may also lead to inability to make connective tissues leading to brittle bones.
Type III Ostegenesis Imperfecta
Image source: pediatricsconsultant360.com
Types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfect include eight types. There are varying severities as well as the gene involved in these types of the disease. These are:
Type I
Type I OI is the most prevalent type and it is considered the mildest form of OI. The structure of the collagen is usually normal, but there is insufficient number of the collagen leading to weakening of the bones.
Type II
Type II OI is considered the most severe type of OI. This is due to the defects in the collagen formation. Patients with this type have severe brittleness of the bones that may result to fractures even before birth. This type usually does not support life and fetus may not survive.
Type III
Type III OI involves adequate collagen, but they are improperly formed causing bone deformities and other complications.
Type IV
Type IV OI is considered moderately severe. Just like Type III, the collagen is of sufficient quantities, but has poor quality.
Type V
Type V OI has similar features than Type IV. Type V has characteristic mesh-like appearance of the bones under histological examinations.
Type VI – Type VI is also similar to Type IV with a characteristic of fish-scale bone.
Type VII – This type is recessive in nature and was recently discovered.
Type VIII – Type VIII is similar to other types similar to LEPRE 1 gene.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Symptoms
The severity of symptoms often differs according to type. Common symptoms include:
- Weak bones
- The classical symptom of osteogenesis imperfect is weak bones due to defects in the collagen matrix that helps strengthen the bones. Patients usually suffer from fractures even in the absence of high-impact tension.
- Short stature
- The growth of the long bones is also impaired because of collagen defects.
- Breathing difficulties
- The bones in the rib cage may be weak leading to inability to expand during inspiration.
- Triangular-shaped face
- The cranium may also be affected leading to problems in the formation of the facial bones.
- Hearing loss
- The small bones in the ears responsible for vibrating and transmitting sound waves is also weakened and may be fractured leading to permanent hearing loss.
- Bone deformities
- The weak bones is unable to support the normal structure and position of the bones and may also not be able to efficiently bear the weight of the patient leading to deformities such as scoliosis and bow-leg.
- Brittle teeth
- The teeth are made up of strong collagen matrix in order to become strong. As a result of OI, the teeth may become weak and prone to cavities.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Pathophysiology, Genetics, Causes
Osteogenesis imperfect results from autosomal dominant inheritance of gene defects of connective tissue formation. However, more recent studies have also found some cases of autosomal recessive in nature. OI can be inherited from parents, but some cases may also be a result of sporadic or individual mutation without the factor of inheritance.
The defect in the Type-1 collagen gene results in the substitution of the amino acids to a bulkier amino acid in the collagen helix. Because of the larger amino acids, there is hindrance that creates a bulge in the collagen creating a defective collagen structure. The presence of improper collagen makes the structure of the bones brittle.
Genetic predisposition is very strong; however, some patients may have developed the gene mutation themselves and may stop functioning adequately.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Diagnosis
The diagnosis of OI starts with a thorough physical examination including the teeth and the eyes. Presence of family history of osteogenesis imperfect may also be determined. Other tests essential for diagnosing OI include:
X-rays
X-rays provide a clear image of the bone structure and other malformations. Patients usually exhibit one or more stress fractures on the skeletal system.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing may be performed to identify the specific genetic mutations.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound may be also performed when the mother is pregnant to determine OI in utero. Severe cases of OI may be detected from the fetus using ultrasound.
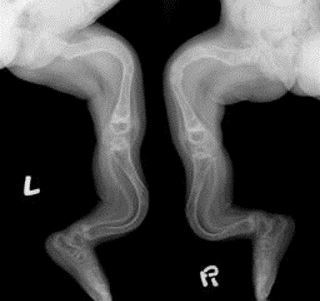
X – ray imaging showing long bone deformity
Image source: physio-pedia.com
Treatment
There is no cure for osteogenesis imperfect because of the genetic mutation. Treatments involved are only supportive to enhance the bone strength, maintain mobility and prevent fractures. These include:
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used to improve the mobility and strengthen the muscles thereby enhancing the shock absorbing property of the muscles to prevent bone injuries.
Exercise
Regular weight –bearing exercises help in increasing the bone density of patients.
Proper diet
Diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential in improving the bone density and prevent further osteoporosis. Vitamin D and calcium supplements may also be given.
Mobility aides
Mobility aides are used such as wheelchairs, crutches and grabbing arms to improve autonomy and mobility of patients.
Biphosphonate therapy
Biphosphonates in the form of oral alendronate or intravenous pamidronate and zoledronic acid are also increasingly used for OI to increase the bone mass. Side-effects of these medications include nausea, bone pain and dizziness. However, therapy with pamindronate can also lead to weakness of bones so regular bone density determination is required.
Surgery
Surgery serves as a last resort for the treatment of OI. Metal rods can be inserted in the long bones to increase strength and serves as support. Metal rods also increase in length as the child grows to support the growing bones.
In cases of severe scoliosis, spinal fusion may be done to correct the spinal deformity. Spinal fusion involves the realignment and fusing of the spinal bones.
Prognosis
Prognosis of OI depends on the type and severity of the symptoms. Patients with Type I have a better prognosis. On the other hand, those that have Type II OI may not survive at birth. The most common cause of death is respiratory failure and accidental trauma. Those who are treated often live normal lives.
Life expectancy
The life expectancy of patients with OI is indefinite; however, statistics shows that more than half of cases die before the age of ten. Those who reach more than this age usually have better outlook.