Esotropia – Pictures, Definition, Surgery, Treatment
What is Esotropia?
Esotropia, a form of strabismus, which occurs when there is a misalignment of the eyes which is distinguished as a convergence of the visual axes which is done excessively leading to an appearance of “cross eye”. What happens is that the lateral muscles of the rectus are paralyzed which resulted to one eye being abnormally deviated inwardly, towards the person’s nose, which is observed during an attempted gaze.
There is actually visual signal suppression from the eye to the brain which results to having the decline depth of perception. While the other eye functions normally. This is a common ocular disorder found in infants.

Misalignment of the eyes or Esotropia
Symptoms of Esotropia
Persons diagnosed as having Esotropia are unable to use both eyes together especially when gazing at a particular object. The popular symptoms manifested by a person having this ocular disease condition are as follows:
- Double vision or strabismus
- Decreased vision
- Misalignment of the eyes
Aside from this, you might observed that persons with this ocular condition, are found to squint often during bright sunlight or are found to tilt their heads towards one direction just to be able to use their eyes together. They often will rub their eyes in a repeated manner. Children, who comprise the most numerous number of reported esotropia, will at times not be able to tell you that they are experiencing the symptoms mentioned. However, you might observe that they close one eye, usually the eye that is impaired, to be able to compensate for the visual problem. You might also notice a faulty perception to the objects that are presented to them.
The brain of a child, having double vision or strabismus, ignores the image of the misaligned eye and will only constantly use the other functional eye. This is called as the lazy eye or amblyopia. They often experience such condition associated with this kind of ocular problem. However, with adults, lazy eye is easier to pinpoint since the brain is trained to accept the images coming from both eyes and it can’t ignore the image from the impaired eye.
Causes of Esotropia
This ocular condition may be due to the fact of the following the common reasons:
Refractive Errors
There is an occurrence of refractive errors because the focus of the light by the eye is incorrect.
Insufficiency in Divergence
There is an insufficient divergence since the person doesn’t see the distant objects clearly.
Excess Convergence
There is excess in convergence or what is termed as strabismus, is usually seen when the eyes fail to look at the same direction.
Other causative factor that may lead to having esotropia includes:
- Damage to the sixth cranial nerve
- Genetic disorders
- Optic Nerve Hypoplasia
- Deficient in Glycerol Kinase
- Bilateral Frontoparietal Polymicrogyria
- Carbohydrate deficiency in Glycoprotein Syndrome type 1a
- Tumor
Diagnosis of Esotropia
The physician usually does the diagnosis of this ocular condition. What the physician usually does is that he or she first identifies this disease as a pathological. The first six months, is when the infantile esotropia develops. As stated above, esotropia is usually found in infants. However, the disease may be transient, going on and off, which will delay diagnosing this ocular problem.
Second, the physician will measure the eyes through the alternate prism test. It will measure the angular deviation of the eyes. An angle of 20 prism diopters means that the patient is positive with infantile esotropia. When it falls between 20 to 40 prism diopters, there is still a chance to resolve the ocular problem. However, when the angle falls to 40 prism diopters and above, it is expected that it will rarely resolve by itself.

Alternate prism test to measure the angular deviation of the eyes
Third, the physician will check for amblyopia or for crossing of the eyes. After that, he or she will check for additional signs of ocular motor problems such as incomitance, impaired binocularity, and scotomas. Lastly, the physician will look for other additional underlying etiology of esotropia.
It is important to note that the physician will do tests to be able to know the strength of the muscles located in the extraocular area. Such test includes:
- Visual acuity
- Standard ophthalmic exam
- Retinal Exam
- Neurological Examination
Esotropia vs. Esophoria
The main difference between Esophoria and Esotropia is that in Esophoria, the eye is deviated inwardly with is associated with an imbalance in the extra-ocular muscles. It is a convergent strabismus or a squint. It is often constant and is reported to be present before the school age, usually in the ages 2 and 3 years old. Meanwhile, Esotropia, there is a possibility of fusion and diplopia or having double vision is uncommon with this disease.
Treatments of Esotropia
There are actually many options in treating Esotropia. This treatment can be either:
- Optical Correction – Most often, this optical problem can be primary treated with the use of corrective glasses. The ophthalmologist, a physician specialized in vision and eye care, will prescribe the glasses that is designed to treat the impaired eye.
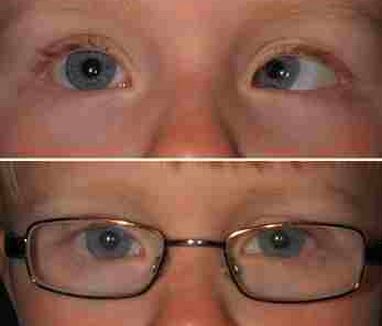
Optical correction for esotropia
- Added Lens Power – Some practitioners would suggest overplussing the child. Overplussing the child is done through using an additional plus power added to the singular vision lens.
- Prisms – As mentioned earlier, this test will measure the angular deviation of the eyes.
- Active Vision Therapy – It is done through the use of penlights and mirrors, biofeedback, tracing pictures, puzzle completion, and video games. Electronic optical instruments may be used to enhance the therapy.
- Pharmacological Agents – Some Physicians will prescribe medications to treat Esotropia; such of this treatment includes miotic medications.
- Chemodenervation – Chemodenervation treatment is usually done by injecting Botox or Botulinum Toxin. It is injected in the extraocular muscles. It will help in relieving the strabismus found in Esotropia
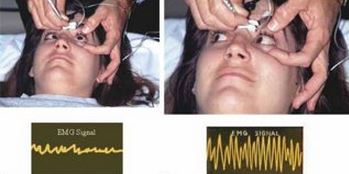
Chemodenervation Treatment
- Surgery – Lastly, if all the other treatments mentioned didn’t succeed, surgery is considered the last most effective option. The surgeon will correct the underlying disorder by correcting it through surgical operation.