Flesh Eating Disease – Pictures, Symptoms and Treatment
What is Flesh Eating Disease?
Flesh eating disease is also known as necrotizing fasciitis, which means decaying skin. It is a rapid progressing type of bacterial infection that destroys the skin, fat and tissue that covers the muscle in a short time span, within 12 to 24 hours. Actually, the flesh is not eaten but the skin is dying as a result of the infection that the person has.
The bacteria, associated with this disease, cuts off the blood supply. Hence, the tissues die and go through the process of decay, medically termed as necrosis. It is caused by a bacterium; group A beta hemolytic streptococci which is common culprit in this type of disease, which targets the layers of tissue, which is termed medically as fascia, in your muscles. It is a serious and very rare disease condition. In occurs in 1 out 4 people.
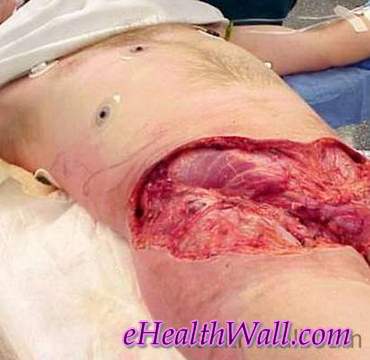
Picture 1 – Flesh eating disease at groin
How do you get Flesh Eating Disease?
There are many different ways in acquiring the bacteria which causes the disease condition. The one common reason is when the culprit bacteria enters your body through an open wound, from a burn, a cut, surgery, or an insect bite. You can also get it:
- When one has surgery sites or in tumors or in gunshot wounds
- when one has muscle strain or bruise
- Wounds coming in contact with saltwater fish, oyster which are both raw and ocean water or when you are handling animals from the sea like crabs.
- When one has a weak immune system
- When one is suffering from chronic disease in the heart, lungs, or liver disease.
- When one has recent contact with someone who is positive with the disease condition.
- When one has chickenpox, all though not all having chickenpox ends up with this disease condition.
It is important that you keep in mind that this flesh eating disease occurs very rarely. So even if you have the factors mentioned above, the chances of acquiring it is low.
What causes Flesh Eating Disease?
The necrotizing fasciitis is caused by many bacteria. Some of these bacteria are proven to cause infections like impetigo or strep throat. This kind of bacteria causes mild form of infections. In rare case, it can result to a much more dangerous infection
Is Flesh Eating Disease Contagious?
This disease, which is somewhat contagious, can be passed from one person, who has an immune system that is low, to another by mere close contact, through kissing, touching the infected wound, or when an infected person cough or sneeze, with the one who has the bacteria. The patient having the disease condition is not likely to be contagious and the transmission points are through objects that are inanimate in nature.
Flesh Eating Disease Symptoms & Signs
Early recognition of the symptoms associated with this disease includes the following:
- Altered Mental State. Toxic effects of these bacteria can result to disorientation, confusion or mental dullness. When the bacteria have spread to the bloodstream, shock can develop and in the long run can lead to coma.
- Pain. An early sign of this disease condition is severe pain. This is due to the fact that the nerves in the affected area are dying; hence there is poor circulation of blood, leading to pain.
- Heart Palpitations. Infection and High Fever leads to increase heart rate, which is leading to heart palpitations.
- Local Skin Warmth. The affected area appears, initially, red and is hot to touch. The inflammatory process is triggered. You must take note that the skin changes from red to purple to dusky gray.
- Swelling. The area infected is swollen plus the skin is shiny and taut. It usually takes place within 30 minutes.
- Blisters. A popping and crackling sound is produced when you press the skin, blisters formation may accompany it.
- Foul Odor. When the skin and soft tissues go through the dying stage, it will eventually produce a foul odor that emanates from the wound.
- Ulceration. There is an opening of the skin which is developing when the infected tissue of the skin dies.
- Malaise. Extreme fatigue along with headache, nausea and generalized weakness is another symptom if this disease condition.
- High Fever. Chills and sweating are common along with high fever which runs through 38.9 to 40.6 degrees Celsius or 102 to 105 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Dizziness. The disease causes blood pressure that is low which results to the feeling of fainting or being dizzy.
Flesh Eating Disease Treatment
Once there is a confirmed diagnosis, steps must be taken as soon as possible. When the treatment is not done or undertaken, this disease condition can be fatal.
Surgery
The primary step is debridement of the infected area which is done surgically.
Medication – Antibiotics
In addition, antibiotics are given intravenously which should be administered as soon as suspicion arises.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
This helps in prevention of tissue necrosis or death and aids in the promotion or recuperation.
Early treatment is necessary. The sooner the infected area is treated, the more likely you will avoid complications that are serious and will recuperate from the bacterial infection.
Flesh Eating Disease Prevention
There are two important things you have to remember to prevent acquiring this disease condition:
Seek medical attention. If you suspect someone or manifest the symptoms that have been mentioned above. You can take antibiotics also as a precautionary action.
You should take good care of any minor cuts or wounds. Wash the infected area with soapy warm water, keep it always dry and clean and always cover it with bandage.
Flesh Eating Disease Pictures
Here are few pictures of flesh eating disease
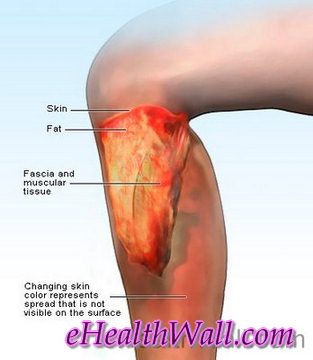
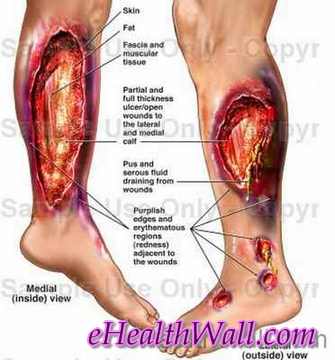
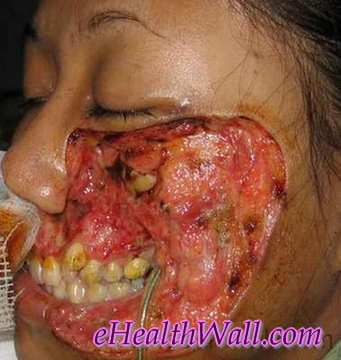
Picture 2 – Flesh eating disease on face
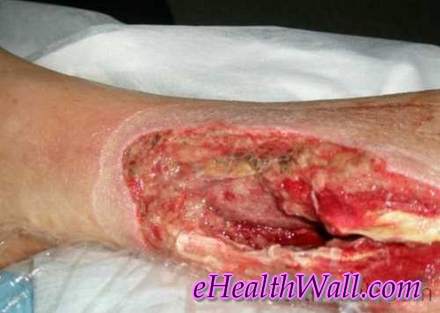
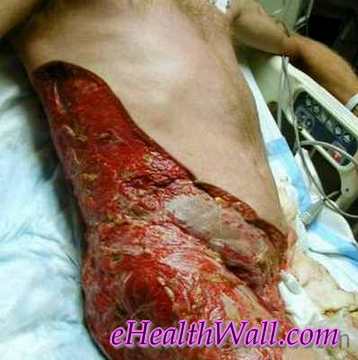
Picture 6 – Flesh eating disease on right side of chest, abdomen & thigh