Prurigo Nodularis – Treatment, Causes, Symptoms and Pictures
What is Prurigo Nodularis?
In layman’s terms, it means “bumps that are itchy”. It is a skin disease, which appears on the legs, arms and elsewhere in the body, which has a characteristic of nodules that are pruritic or itchy. It is also known as Hyde Prurigo Nodularis, PN, Lichen Simplex Chronicus, Picker Nodules, Lichen Corneus Obtusus, and Neurodermatitis Circumscripta in an atypical nodular form. The middle-aged to elderly persons are often the persons affected by this kind of skin disease. It is a chronic kind of inflammatory dermatosis or skin disease that results to papulonodular eruption. It has a characteristic of pruritus in a severe form, nodules and papules with ulcerations and excoriations with is because of too much scratching.
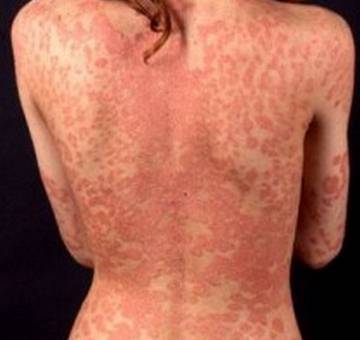
Picture 1 – Prurigo Nodularis in women
Causes
The main etiology of why the Prurigo Nodularis exist in some persons is, up to this point, still unknown. Researchers found out that the following factors may induce the skin disease called Prurigo Nodularis, such of these factors include:
- Fungal infections
- Poor diet
- Yeast infections
- Toxin
- Allergic disorders
- Poor liver function
- Psychiatric Illness such as delusion of parasitosis
- Parasites
- Thyroid disease
- Linear IgA disease which is an autoimmune disease condition
- Becker’s Nevus
It has also been associated and linked with the following disease conditions:
- Hodgkin’s disease
- Uremia
- Polycythemia rubra vera
- Thyroid disease
- Cholestasis
- HIV
Symptoms & Signs
When a person, at around 20 to 60 years old of age, is diagnosed with Prurigo Nodularis, he or she may manifest the following signs and symptoms:
- Small red bump (early sign)
- Brown, hard globular nodules
- Bumps
- Itching usually occurring at anytime but it most often occurs in the late evening and night
Diagnosis (Histology)
The best way to diagnose this kind of skin disease is done through:
- Skin biopsy
- Lesion biopsy which shows elevated eosinophils
- Culture that is needed to rule out any infection especially staphylococcus infection which is linked to atopic dermatitis
- Histopathology or Histology
Histology is the study of anatomy of the cell, which in this case is a human cell, under the microscope. Upon the histopathological exam, with the person diagnosed with this disease condition, will revealed orthokeratotic acanthosis and hyperkeratosis. With focal parakeratosis, under hyperkeratosis, there is an irregular acanthosis. The rete ridges are irregular and elongated with an infiltrate dense dermal that consists of eosinophils, histiocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes. The appearance of pseudoepitheliomatous or pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia comes from a downward, irregular epidermis proliferation, severe papillomatosis and adnexal epithelial structures.
With the focused turned into the dermis’ papillary, there is an observed elevation of fibroblast that is multinucleated with thick fiber collagen bundles that are arranged to the surface, perpendicularly. There is also an observation of proliferation of the Schwann cells and nerve fibers. In some areas, they are vertically-oriented and dilated capillaries. Found at the surface, located in the interstitial spaces and around the vessels are moderately dense lymphocytes, isolated mast cells, eosinophilic granulocytes, macrophages, melanophages, dermal dendritic cells or hemosiderophages with erythrocytes that are extravasated. You can also find in patients diagnosed with atopic diathesis, eosinophilic granulocytes that are degranulated. Crusting seen around the margin with parakeratosis and exudates maybe found where there is a presence of excoriations or erosions and when there are neutrophils and plasma cells.
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions that have similar appearances or the differential diagnosis with Prurigo Nodularis are the following conditions:
- Impetigo
- Insect Bites
- Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis
- Aphthous Stomatitis
- Bechet Disease
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Allergic contact Dermatitis
- Lichen Ruber Verrucosus
- Lupus erythematodes hypertropicus et profundus
- Linear IgA Dermatosis
- Dermatitis Heretiformis
- Pemphigoid Nodularis
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Chancroid
- Chrug-Strauss Syndrome
- Ecthyma
- Lymphoma
- Pseudolymphoma
- Cutaneous metastases
- Keratoacanthoma
- Dermatofibroma
- Ictus Reactions
- Prurigo Pigmentosa
- Actinic Prurigo
- Polymorphous light eruption
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Ecthyma Gangrenosum
- Herpes Simplex
- Wegrener Granulomatosis
- Verrucuous carcinoma
- Hypersensitivity Vasculitis or Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis
- Venous Insufficiency
- Sporotrichosis
Treatment
It is a challenge when the person will undergo treatment for Prurigo Nodularis. The treatment goal for this skin disease condition are to develop an individualized treatment scheme and topical and the usage of causal, systemic and topical therapies
Causal Therapy
The treatment of the causative agent of this skin disease condition may be effectively done once the person undergoes extensive examination and testing and having a careful diagnosis to be able to eliminate and detect the cause that triggers the pruritus. The therapy is specific when the causative agent is made known.
Symptomatic Treatment
However, if the symptoms of pruritus can’t be stopped or eliminated or if the causative agent is not made known, then the treatment goal will be to interrupt the pruritus which may be accomplished through symptomatic treatment. The medication or treatment aims for pruritus or itchiness reduction leading to the improvement of the Prurigo Nodularis. Such of these symptomatic treatments includes:
Topical Anti-pruritic Therapy
Topical corticosteroids medications are often prescribed with this kind of skin disease condition. Topical medications are drugs which can be applied in the patient’s affected skin. Other topical medications may include the following medications: Calcineurin Inhibitors, Vitamin D3 Analogues, Menthol and Polidocanol, Capsaicin, Cannabinoid agonists, and Phototherapy.
Systemic Anti-pruritic Therapy
Systemic treatments are drugs which the patient ingests or is injected to the patient. Examples of these drugs includes: antihistamines, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine, opioid receptor antagonist, thalidomide and roxithromycin with tranilast. The most essential medication for systemic anti-pruriginous agents are the antihistamine drugs.
Other Therapies
Other treatment that may help in treating the Prurigo Nodularis skin disease may be as follows: Cryosurgery, Laser, and Psychotherapy. The most widely used in treating the Prurigo Nodularis is the Cryosurgery. There is a need for psychotherapy treatment or psychosomatic and psychiatric treatment especially when there is a psychiatric or psychosomatic disorder has been diagnosed together with the skin disease disorder such as Prurigo Nodularis.
Pictures
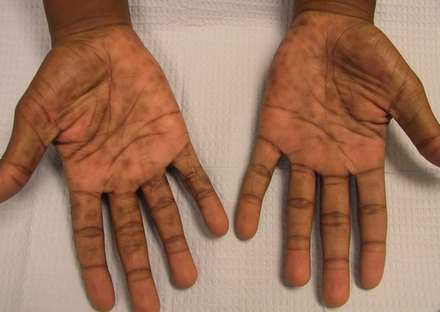
Picture 2 – Prurigo Nodularis on hands
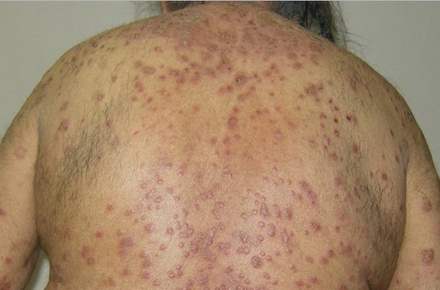
Image Source -askdrshah.com
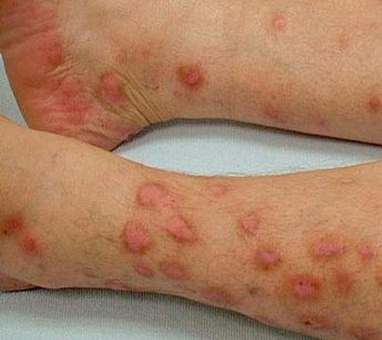
Picture 4 – Prurigo Nodularis on legs
image source – mf.cz