Agranulocytosis
What is Agranulocytosis?
It is otherwise known as granulopenia, granulocytopenia or agranulosis. It is sometimes interchanged with the medical term neutropenia. It is a medical condition or term, which is derived from a Greek word that means “without granulocyte”, that suggest a reduction in the production of granulocytes, which is a blood disorder, under this classification includes subtypes such as basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils.
Granulocytes are actually a kind of WBC or white blood cells. When a person has or is experiencing Agranulocytosis, he or she is at great risk to acquire infection as well as mucosal ulceration. Without these cells, the body is unable to fight off the infection.
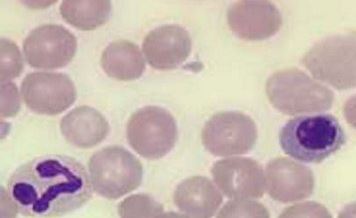
Agranulocytosis Image
Image source: loroati.com
Agranulocytosis Symptoms
Persons that have Agranulocytosis will experience the following symptoms:
- Weakness
- Ulcers in the person’ s stomach, bowels or mouth
- Chills
- Fever
- Rigors
- Fatigue
- headache
- Sore throat
- Opportunistic Infection to any organ such as the throat, rectum, mouth, vagina, or nose
- Septicemia (in the long run or as the condition worsens)
Although the symptoms mentioned above are associated with Agranulocytosis, still some of the persons who reportedly suffer from this kind of condition reports to have no symptoms or are asymptomatic during the illness period.
Agranulocytosis Causes
The etiological reason or cause of why Agranulocytosis occurs may be due to the following reasons or causes:
- Chemotherapy effect
- Diseases that affects the bone marrow
- Hereditary diseases
- Radiation therapy side effects
- Having autoimmune diseases
- Taking in prescriptions which have a side effect of Agranulocytosis such drugs like antineoplastic, sulfonamides, psychotropic and chloramphenicol.
Agranulocytosis Diagnosis
In diagnosing the patient with Agranulocytosis, the person will undergo examinations such as:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Complete blood count examination that includes differential which measures eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils
- Genetic examination
- Blood examinations may be done through bone marrow biopsy through the special procedure called FNAB or fine needle aspiration biopsy
The important and confirmative examination with regards to diagnosing the person disease is laboratory values. It is consider as the main indicative measure especially when person is experiencing Agranulocytosis. The laboratory values will depict a lower number of cell counts of the granulocytes, which is considered to be abnormal in nature and which are indicative of Agranulocytosis. The normal laboratory values will differ from one hospital to another it is advisable that the normal laboratory values in a particular hospital is to be followed to be accurate in diagnosing Agranulocytosis.
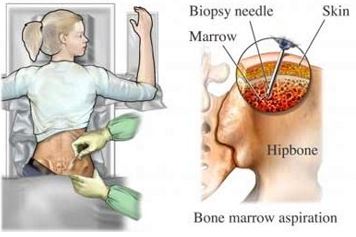
Bone Marrow Biopsy as a confirmative diagnosis for the presence of Agranulocytosis
Image source: drhowell.net
Agranulocytosis Treatment
In treating persons with Agranulocytosis, the causative or the reason must be established first and then the treatment will be based on the cause. If the cause is due to too much intake of medications which can lead to Agranulocytosis, thus, the treatment should be to change or to lessen the medications taken which will need consultation from the trusted physician. Other treatment includes:
- Isolation precaution
- Antibiotics
- Bone marrow transplant
- GMCSF or otherwise known as granulocyte colony stimulating factors
- Stem cell transfusion
With regards to bone marrow transplantation, which is the primary effective treatment for persons that have Agranulocytosis, the criteria must be met prior to undergoing the transplant. The criteria includes matched donor, good health before undergoing the transplant procedure, the age is 40 years old and under.
Agranulocytosis Side Effects & Complications
There are no such thing as perfect treatment, hence we could not forego that there could be complications and side effects that are associated whenever we treat persons with Agranulocytosis. Such side effects and complications include the following:
- Allergic reaction
- High risk for infection
- Bleeding
Hence, by knowing such, we must be able to understand the risk of the treatment provided.