Granulocytopenia
What is Granulocytopenia?
Granulocytopenia is a medical term given that describes the reduction of the granulocytes that are circulating inside the person’s body. The granulocytes include basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils. The basophils are known for inflammatory responses. Meanwhile, the eosinophils are known to act during allergic reaction. On the other hand, the neutrophils which are the most number of granulated form of white blood cells which are functions best in consuming foreign invaders inside the person’s body. It is also associated with eosinopenia, basopenia and neutropenia.
Granulocytes are another term for white blood cells that is covered with granules upon viewing under the microscope, which functions as the fighter against infection. It is found to contain enzymes which digest certain microorganisms. When it reaches the severe form, it is medically termed as agranulocytosis. Hence, it can be sometimes interchanged with granulopenia, neutropenia as well as agranulocytosis.
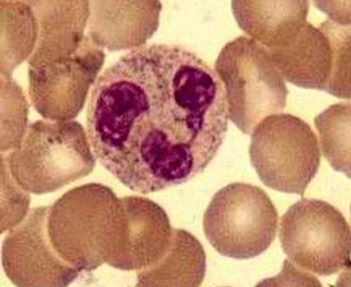
Granulocytopenia Symptoms
Symptoms which are associated with granulocytopenia are considered to be non-exclusive and may lead to other forms of disease condition. It is advisable that you consult a physician for clarity, to allay fear and for further more understanding of the condition that one has. The symptoms associated with this kind of condition include:
- Jaundice
- Sore throat
- Low count on white blood cells
- Fever
- Weakness or body malaise
- Mouth ulcer
- Bleeding gums
- Bacterial kind of pneumonia
- Chills
- Susceptible for infection due to the fact that they experience recurrent infections brought about by bacterial, viral or fungal causes.
- Spleenomegaly (severe kind)
- Petechial bleeding (severe kind)
- Reddish to purplish spots in the person’s body (severe)
Granulocytopenia Causes
Granulocytopenia occurs in an individual because of the following reasons or causes:
- The person has an existing autoimmune disorder
- The person has lupus
- The person has rheumatoid arthritis
- The person has Crohn’s disease
- There is a bone marrow failure
- The person has leukemia
- The person has a current severe kind of injuries
- The person is undergoing chemotherapy
- The person is undergoing radiation therapy
- The person is taking for long term of medications under the classification of antihypertensive, cardiac drugs and antibiotics which are known to lead into acquiring the side effects of granulocytopenia
Granulocytopenia Diagnostic tests
The diagnostic test that one has to undergo to be able to confirm that the person has indeed granulocytopenia includes:
- Physical examination (mandatory)
- Medical history examination (mandatory)
- Urinalysis
- Genetic examination
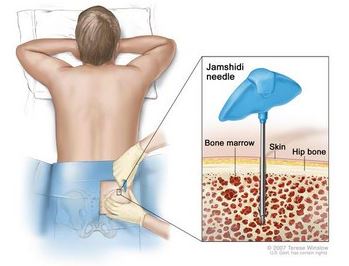
- Bone marrow examination
- Complete blood count examination or Blood examinations with differentiation
- Lymphocyte count examination
- The normal values will differ from one institution to another. Lower than the normal values, especially the ones which deal with granulocytes, given by the medical institution will indicate granulocytopeniaBone Marrow Biopsy to determine presence of granulocytopenia
Granulocytopenia Treatment
The treatment for persons who are diagnosed to have granulocytopenia will consist of:
Pharmacological treatment such as antibiotics
Antibiotics are given to ward off infections which are opportunistic in nature.
White blood cell stimulating factors
As mentioned, granulocytopenia are a form of white blood cells that are low in number to be able to treat it will require treatment that will stimulate the growth of white blood cell.
Leukocyte transfusion
Leukocyte which is another medical term given for white blood cells. Through transfusion process the number of white blood cells particularly the granulocytes will increase and granulocytopenia will be then be hopefully treated if the body responds well to the transfusion given.
The treatments provided are aimed to help the body to bounce back to health and to eradicate the opportunistic infections as well as to increase the number of granulocytes.