Lipohypertrophy – Treatment, Definition, Pictures, Causes
What is Lipohypertrophy?
This is the deposition of fats in the subcutaneous area, usually found at the injection sites of insulin in diabetes mellitus patients. In diabetes mellitus injection sites such as abdominal area surrounding the umbilicus, upper and outer part of the thighs and upper arm and buttocks, these areas contain subcutaneous fats. Subcutaneous layer of the skin, also known as the hypodermis and the superficial fascia, is the usual site for insulin injection because that this area causes less bleeding during the process. In subcutaneous tissue, considered being the best site for insulin injection, the absorption of the insulin is slow progressing thus the patient control of blood sugar is well managed.
Lipohypertrophy particularly affects the adipose tissues in subcutaneous layers. It is in the subcutaneous skin layer where you can find the adipose depots. The formed lumps of adipose tissues and scar tissues collectively called as lipohypertrophy or fatty lump are firmer lumps as compared to other subcutaneous cells. This is a frequent, chronic yet not very serious skin complication seen in diabetes mellitus especially across the area or site with repeated insulin injections. This is the reason insulin injection site rotation is recommended to diabetics.
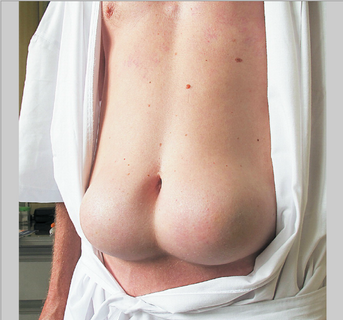
Fatty lumps (lipohypertrophy) either side of umbilicus
Image source: drbriffa.com
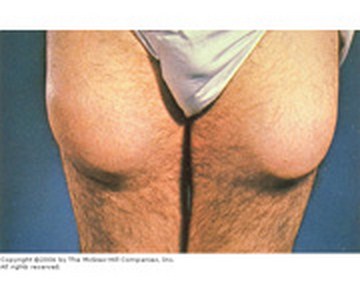
Fatty lumps at legs
Image source: accessmedicine.net
Symptoms
Although most of the time lipohypertrophy or fatty lump is edema-free and pain free, there are also some subtypes of lipohypertrophy that are considered painful ones.
- The most common sign and symptom is a soft lump is felt and seen in areas of repeated injection. Although fatty lumps are seen more frequently in Type 1 diabetes, this can also occur in Type 2 DM.
- There is presence of disproportionate swelling of legs in relation to trunk.
- Fatty lumps are not painful or tender to touch.
- In orthostatism, there is no edema formation.
- Period of hyperglycemia in patients with lipohypertrophied tissues commonly occurs thus leading to unstable DM.
Causes
The disorder of fatty distribution in diabetes mellitus clients are basically because of repeated insulin injection in same spots or the injection sites are too close together. Some children may prick the skin during insulin injection in order not to feel the pain of injection thus not leaving enough space in between injection sites. Although one of the reasons why these clients may be doing the injection on the same areas may be due to the fact that they can’t reach other suitable areas for insulin injection or mainly because of dexterity.
If the needle is not changed frequently and becomes blunt, the injection becomes painful and causes more damage to the integrity of the skin contributing more to the development of lipohypertrophy. When fatty lumps develop more complications may be associated with diabetes mellitus.
In the event that there are already fatty lumps formed then insulin absorption is affected. The insulin plays important role in maintaining the energy level of a person. It is needed in order for the simple sugar be converted to energy. But the presence of lipohypertrophied tissues in insulin injection spots delays the absorption of insulin since these lumps have fewer blood vessels. When this happens the body becomes insulin resistant and can’t convert the sugar into energy. The sugars remain in the bloodstream and eventually are being stored as fats in liver, abdominal area and other parts of the body. There can be increased in abdominal girth due to central fat accumulation in central lipohypertrophy. Buffalo hump or a dorsocervical fat pad and increased breast size in men called gynecomastia.
Furthermore, lipohypertrophy can also occur in person with HIV (Human Immunodeficiency). The protease inhibitors in the meds taken by HIV clients affect the fatty lump formation. HIV protease inhibitors are effective antiretroviral agents. Prolong used of protease inhibitors in the treatment of HIV lead to the development of lipohyperdystrophy that is a metabolic complication in the alteration of fat metabolism. Lipohypertrophy in HIV clients lead to truncal obesity and also affects the insulin leading to complication of diabetes in HIV clients.
Treatment
The primary treatment for lipohypertrophy is to leave it alone for weeks or month. Sometimes it may take a year before the fatty lumps disappear and some cases fat suctioning procedure has been used as a treatment. Another way to get rid of these fatty lumps is proper diet and exercise which are considered the primary important remedies. Increased intake of soluble and insoluble fiber may lessen the development of lipohypertrophy, and so does resistance exercise increase the chance of recovery.
For diabetics who have lipohypertrophy, in order to treat the fatty lumps one must do this is by having an insulin injection rotation scheme, in which the injection sites are rotated in days in a week. Injection in the site with fatty lumps must be avoided since the insulin absorption is decreased on this site. But once you inject insulin in fresher site with no lipohypertrophied tissues lower the insulin concentration by 25% when using rapid acting insulin. Remember that this site will absorb the insulin faster than the previous site with fatty lumps, lowering the dose thus avoiding another complication of DM that is hypoglycaemia.
Here is an useful resource on where to inject the insulin injection