Renal Tubular Acidosis – Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Renal Tubular Acidosis?
Renal tubular acidosis or RTA is a condition wherein there is an accumulation of acids in the body because of failure of the kidneys to perform its function in acid-base balance, specifically to excrete acids into the urine. When blood passes through the kidneys, it is filtered to make the blood clean. The filtrate passes again into the renal tubules for the exchange of acids, salt, and other solutes before urine drains into the bladder to be eliminated. The metabolic acidosis caused by renal tubular acidosis may be caused either by failures in the renal tubules such as in the proximal and distal renal tubules. When there is insufficient reabsorption of bicarbonate ions (alkaline) in the proximal tubule or there is inadequate excretion of hydrogen ions (acid) in the distal tubule, then acidosis may occur. Renal tubular acidosis involves the insufficient urinary acidification in well-functioning kidneys as opposed to the metabolic acidosis that occursin renal insufficiency.
Acidosis occurs when the pH of the blood is below 7.35. It was first described in children by Lightwood and Butler et al. in 1935 and 1936 respectively. RTA in adults on the other hand was first described by Baines et al. in 1945.
Metabolism in the body generates acids as byproducts. Presence of acids in the blood is normal, but an excess of it can lead to disruption of body functions. Acidosis is prevented by the kidneys by excreting acids into the urine and reabsorbing bases or alkaline back into the blood to maintain a normal pH.
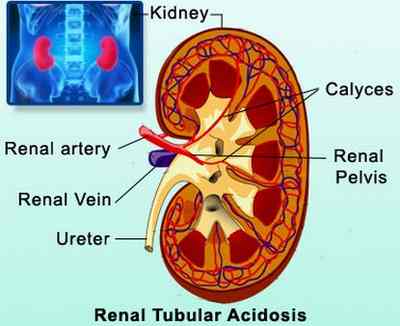
Source – medindia.net
There are different types of renal tubular acidosis depending on the location of failure. These also have varied causes and manifestations. These include:
a. Distal renal Tubular Acidosis or Type 1 RTA
Distal RTA or classical RTA involves the failure of the distal renal tubules to secrete acid in the urine. The inability to excrete acids leads to a non-acidic urine of >5.3. Acids are primarily excreted through the urine. When this is impaired excretion, acidemia or acidosis occurs.
The inability of the cells to excrete hydrogen ions also leads to non-reabsorption of potassium leading to hypokalemia and other electrolyte imbalances.
Causes of distal RTA
- Inheritance – Defects in the distal tubules were studied to be inherited because of abnormal genes present.
- Systemic Autoimmune disorders – Diseases such as Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus also destroy the distal tubules leading to impairment of the functioning of the area.
- Diseases that cause abnormal calcium deposits in the kidneys – Diseases such as sickle cell anemia, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, primary biliary cirrhosis, chronic active hepatitis, analgesic nephropathy, kidney rejection, obstructive uropathy and urinary tract infections cause calcium to build up on the nephrons causing impairment of distal tubular functions.
Symptoms of distal RTA
- Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis
- Urinary stones as a result of alkaline urine
- Hypokalemia
- Nephrocalcinosis
- Bone demineralization as a result of hypophosphatemia (rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults)
b. Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis or Type 2 RTA
Proximal RTA is primarily caused by inability of the proximal renal tubules to reabsorb filtered bicarbonate ions from the urine. The excretion of bicarbonate ions leads to wasting and subsequently, acidemia because there is insufficient alkaline in the blood to neutralize or buffer the acids. The acidosis in proximal RTA is less severe than distal RTA because the kidneys still secrete acids into the urine.
Causes of Proximal RTA
- Fanconi’s syndrome – This is a condition where there is generalized dysfunction of the proximal renal tubules. It is associated with phosphaturia, hypokalemia, glycosuria, aminoaciduria, uricosuria and proteinuria because of the inability of the proximal tubules to reabsorb these chemicals, including bicarbonate ions. Because of phosphate wasting and Vitamin D deficiency, there is bone demineralization (rickets or osteomalacia)
- Cystinosis – Cystinosis is an inherited disorder that disrupts the normal breakdown and use of nutrients. Cystine crystals are deposited in the bones and cause non-reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. Other diseases include Wlison’s disease and fructose intolerance.
- Chemotherapy – Ifosfamide, a chemotherapeutic drug disrupts the functioning of the proximal tubules leading to acidosis.
Symptoms of proximal RTA
Excretion of bicarbonate ions leads to non-reabsorption of other electrolytes giving rise to the following symptoms:
- Hypokalemia (low potassium in the blood)
- Phosphatemia
- Urine pH of 5.5 (alkaline)
- Reduced excretion of Hydrogen ions
- Impaired reabsorption of bicarbonate ions
- Impaired exchange of sodium, potassium and chloride in the distal tibule as a result of aldosterone resistance
Symptoms of Renal Tubular Acidosis
Aside from the specific symptoms discussed earlier, the primary manifestation of RTA is on the level of potassium in the blood. Distal and proximal RTA result in hypokalemia. Potassium is essential for the contractility of the heart and nerve impulse transmissions. A low or high potassium levels result in the following symptoms:
- Weakness, fatigue
- Paralysis
- Dysrhythmias or irregular heart beat
- Anorexia, vomiting
- Abdominal distention
- Leg cramps
- Postural hypotension
- Shallow respirations
- Lethargy and confusion
Causes of Renal Tubular Acidosis
Specific causes of renal tubular acidosis according to type were discussed earlier. General classifications of causes for all types of RTA include:
- Genetics
- Autoimmune diseases
- Hypercalcinosis (calcium deposit build up)
- Drugs or medications
- Other renal disorders
Diagnosis of Renal Tubular Acidosis
RTA diagnosis includes the following tests and exams:
- Acid-base balance examinations – Arterial blood gas studies help in determining presence of acidosis through collection of blood samples on the artery. Urine sample is also taken to check for urine acidity. A high blood acidity and low urine acidity indicates renal tubular acidosis.
- Electrolyte tests – Checking the electrolytes especially the potassium is essential to check presence of hypokalemia or hyperkalemia. Abnormal potassium levels are life-threatening because it cause changes in the contractility of the heart which may lead to cardiac arrest. Other electrolytes include sodium, chloride and phosphate. This identifies the type of RTA a patient has.
Treatment of Renal Tubular Acidosis
Treatment of acidosis focuses on neutralizing the pH of the blood. Electrolyte imbalances are also corrected. Treatment approach includes the following:
- Administration of Alkali – Sodium bicarbonate or sodium citrate and citric acid (Shohl’s solution) is administered daily in divided doses to increase bicarbonate levels and normalize the pH of the blood. However, administration of bicarbonates also leads to further hypokalemia so potassium replacement should be instituted. Treating acidosis prevents renal failure and calcium stone formation. Alkali therapy also reverses problems on sodium, chloride and phosphate abnormalities.
- Potassium Replacement – Potassium is given to correct hypokalemia. In cases of type 4 RTA with hyperkalemia, diuretics such as furosemide may be given to excrete excess potassium levels in the blood.
- Hydrochlorotiazide Diuretics – Hydrochlorothiazide are special kid of diuretics that allows reabsorption of potassium in the tubules leading to increase in potassium levels during bicarbonate therapy because administration of bicarbonate leads to more excretion in the urine of bicarbonate ions and potassium.
- Phosphate and Vitamin D therapy – In cases of Fanconi’s syndrome in proximal RTA, Vitamin D and phosphate should be replaced to prevent bone deformities such as osteomalacia and rickets
Prompt management of RTA prevents further complications and renal failure.
Complications of Renal Tubular Acidosis
Renal tubular acidosis results in the following complications as a result of interplay of electrolyte imbalance, calcium formation and Vitamin D deficiency:
- Bone disease. Hypophosphatemia leads to bone demineralization because phosphate is responsible for calcium resorption in the bones. Inability to maintain calcium in the bones leads to bone breakage and calcium stone formation in other parts of the body.
- Growth retardation. The occurrence of rickets and osteomalacia result in retarded growth.
- Kidney stones. Calcium deposits as a result of alkaline urine and hypophosphatemia eventually lead to kidney stone formation which may potentially lead to renal failure.
- Renal Failure. This is the result of RTA when treatment is not done to correct the condition.
Prevention of Renal Tubular Acidosis
Prevention of RTA includes measures to prevent the causes. It is essential to maintain good hydration by increasing fluid intake to prevent stasis of byproducts in the kidneys. Avoiding highs salt diet is also essential to prevent overworking the kidneys to regulate sodium levels. Ensure adequate exercise to prevent calcium stasis and stone formation. Genetics, inheritance and certain autoimmune diseases that lead to RTA cannot be prevented so supportive managements should be implemented to maintain healthy kidneys.