Pregnancy Symptoms Week by Week
Pregnancy symptoms week by week is one of the concerns of pregnant women because they want to know what is happening to their bodies as well as what is happening inside their womb. This article discusses the pregnancy symptoms week by week as well as the fetal development week by week. It shows the possible pregnancy symptoms week by week in order for expecting mothers to expect and prepare for the changes throughout pregnancy. The most important thing of knowing the changes throughout pregnancy is to maintain a healthy one with good pregnancy outcomes.
Pregnancy Symptoms week by week
Week 1
Maternal Changes – During this week, the body is getting ready for ovulation.
Fetal Development – There is still no fetus that is developing, but the ovaries are starting to develop a mature egg cell for ovulation.
Recommendations: Women planning to have pregnancy should start taking iron and folic acid supplements as soon as the last menstruation has ended in order for the body to prepare for possible pregnancy during the next cycle. It’s also nice to know the exact date of ovulation through menstrual calendars in order to determine the right time to conceive.
Week 2
Maternal Changes – The uterus has just developed the uterine lining in time that the egg cell will be fertilized by a sperm. During the time of ovulation, women may feel a sharp pain on side of the lower abdomen as a sign of egg cell rerelease known as mittleschmerz as a sign of pregnancy symptom week by week.
Fetal Development – The ovum is now released in the fallopian waiting for a sperm cell for fertilization.
Week 3
Maternal changes – Fertilization has just occurred after a successful sexual intercourse. There may be signs of implantation because the zygote or the fertilized egg implants at the lining of the uterus. Spotting during this time should not be mistaken as menstruation. Mothers should abstain from drinking alcohol and smoking because these may have effects on the growing embryo. Smoking during pregnancy may bring about problems in fetal development. The mother’s body also releases early pregnancy factor to prevent the body from attacking the embryo as a foreign body.
Fetal Development – The zygote divides rapidly as it travels along the fallopian tube into the uterus for implantation. The zygote usually travels to the uterus for 4 to 7 days. Cell division occurs until it becomes a blastocyst. On day 10, the blastocyst has successfully implanted. Once implantation has occurred, the zygote is now known as an embryo.
Week 4
Maternal Changes – During this time, a pregnancy test will usually yield a positive result due to increase in a hormone called HCG or Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. Women may also start feeling presumptive signs of pregnancy such as mood swings, frequent urination, tender breasts and feelings of tiredness.
Fetal Development – The first trimester is the most crucial stage for the fetus because organogenesis happens or the development of the organs. The 4th week of pregnancy reveals a yolk sac that acts as a placenta.
Week 5
Maternal Changes – Pregnant women may start feeling headaches, crampy uterus and morning sickness. This usually persists until the end of the first trimester.
Fetal Development – The heart of the bay begins to beat early during this week. This may be apparent in ultrasounds. The head and the tail of the baby are also distinguishable. The neural folds also begin to fuse to form the spine. The average length of the fetus is now 1.5 to 2.5 mm.
Week 6
Maternal Changes – The morning sickness may get intensified during this week because of continuous rise is maternal hormones. The areola will also start to appear darker and bigger. Avoid cleaning the cat litter to prevent toxoplasmosis that can result in fetal abnormalities.
Fetal Development – The larynx and the inner ear start to appear. The limbs also develop as buds. The heart begins to bulge and the circulation is well established. The placental lining is still forming. The primordial of the stomach, lungs, pancreas and liver may also be evident.
Week 7
Maternal Changes – Chloasma or melasma start to appear because of increasing pregnancy hormones.
Fetal Development – The baby is about 7 to 9 mm during this stage. The hand plates are present and the genital tubercle is also developing, but it is still hard to distinguish if the fetus is a boy or a girl.
Week 8
Maternal Changes – Regular prenatal check-ups start at this week. The maternal symptom such as morning sickness, feeling of tiredness and breast tenderness still persist.
Fetal Development – The length of the baby is 8 to 11 mm from crown to rump. The hind brain of the fetus is visible, the gonads will differentiate into either ovaries or testes and there is spontaneous movement, but the mother may still not feel it. Hardening of the bones also starts during this stage and elbows start to appear. The toes may also have developed by now.
Week 9
Maternal Changes – Mothers may begin feeling stuffy nose because of increased progesterone in the body. Nose bleeding and nasal congestion may be normal during this stage.
Fetal Development – The fetus already has distinct elbows by now. The length will be about 13 to 17 mm. The average weight will be also 1 gram. The gonads of the fetus have already developed.
Week 10
Maternal Changes – The abdomen may begin to enlarge a little as a pregnancy symptom week by week during this time. The waistline will slowly disappear and linea nigra, a black, thin line from the umbilicus to the symphysis pubis, may develop. This integumentary change may eventual disappear weeks after delivery.
Fetal Development – The embryo now becomes a fetus during the 10th week of pregnancy. It has grown to 25 to 35 mm in size and increases weight to 4 grams. There are already evident tiny toes. The eyes may be largely open; however, the eyelids may still begin to fuse. The genitals of the fetus may also start to differentiate, but still not distinguishable. The upper lip and the external ears also have formed. The tail of the fetus already has disappeared during this stage.
Week 11
Maternal Changes – Gaining weight starts to begin during this stage. The normal weight gain for pregnant women is 1 to 2 lbs a month. Healthy diet is a key to prevent excessive weight gaining.
Fetal Development – The head of the baby is actually 3 times larger than the body. The fingernails may appear during this week and the iris of the eyes is developing. The average weight of the fetus during this week is 7 grams.
Week 12
Maternal Changes – The early symptoms of pregnancy such as nausea and extreme tiredness usually fade away as the first trimester ends. The abdomen will also start to appear bigger. The placenta has been fully developed and it takes the place of the corpus luteum in producing maternal hormones. Risk for miscarriages is reduced at the end of the third trimester.
Fetal Development – The structure of the brain is now similar to the brain at birth. The liver starts to secrete bile during this week. The average weight doubles from the previous week to 14 grams. The length will now be 3.5 inches. The reflexes also appear. Doppler may be able to detect the heart beat of the fetus.
Week 13
Maternal Changes – This is the beginning of the second trimester. During this time, the mother feels stronger because of absence of morning sickness and other uncomfortable feelings. Pregnancy starts to become real for spouses.
Fetal Development – The complete set of baby teeth has developed, but still has not erupted until the 6th month of extrauterine life. The average weight is 28.3 grams. The placenta also continues to grow. The intestines begin to migrate into the abdominal cavity. Insulin has also stared to be secreted by the pancreas. The presence of diabetes in mothers may be detected by the pancreas of the fetus, which secretes more to cope with the maternal blood. The fetus’ stool or meconium also begins to develop on the intestines.
Week 14
Maternal Changes – Chloasma is starting to be more apparent during this time as estrogen and progesterone continues to increase. The linea nigra may be darker and more apparent as well as the areola also starts to become bigger.
Fetal Development – The size of the fetus is now 12.5 cm. The kidneys are actually producing urine. The urine may mix with the amniotic fluid. The fetus starts to ingest the amniotic fluid and eventually excretes it through the urine.
Week 15
Maternal Changes – The heart increases cardiac output to compensate with low hemoglobin levels and to supply the baby with blood through the placenta. There is also increasing weight and the usual clothes may not fit well anymore. Detecting fetal abnormalities through blood tests such as Alpha-fetoprotein determination can now be done.
Fetal Development – The skin of the fetus is very thin with visible blood vessels. The average weight is about 70 grams. The heart begins to pump more blood of about 25 quarts of blood in a day. The hair pattern on the scalp also develops.
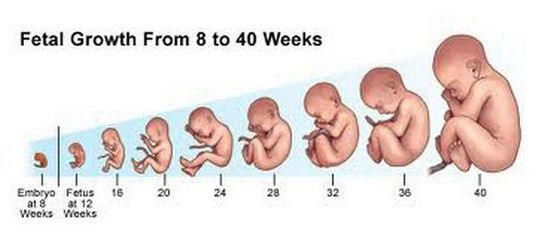
Pregnancy symptoms week by week picture
Fetal development week by week
Week 16
Maternal Changes – Women may have increased sexual drives because of very high maternal hormones. Modifications in positions may be necessary, but generally, sexual intercourse is not prohibited during pregnancy.
Fetal Development – The eyelashes and the eyesight of the fetus have already developed during this stage and the nails in the fingers and toes have started to grow.
Week 17
Maternal Changes – The fundus of the uterus is now between the navel and the symphysis pubis. The vaginal secretions, sweating and nasal congestion may increase normally.
Fetal Development – Brown fats are starting to develop at the skin. Brown fats help fetus maintain normal body temperature when they are born. The average weight is now 142 grams. Startling reflex may be apparent when the fetus hears loud noises on the outside world.
Week 18
Maternal Changes – Since the uterus may compress other organs when you lie down, women now start to sleep harder. Sleeping with more than one pillow usually relieve this feeling. Increased urination is also more intense as the growing uterus pushes into the bladder.
Fetal Development – The fetus is growing rapidly during this stage. The bones still continue to harden. The fingerprints may be well developed and the pads of the toes and pads are developed.
Week 19
Maternal Changes
Heart burn and indigestion may be a special problem starting this week because of slowed intestinal motility and gastric emptying as a result of maternal hormones. Staying upright after eating is a remedy to prevent heart burn.
Fetal Development
The ovaries of female fetuses normally may have developed primitive egg cells during this time. Fine hair called lanugo also grows in the skin of the fetus. Lanugo normally lessens as the baby reaches term.
Week 20
Maternal Changes – This stage may make mothers excited because they are halfway over pregnancy. The navel may start to prop out because the growing uterus pushes out the belly button. There is also increasing difficulty of breathing as the uterus pushes against the diaphragm. During this time, the fetus may have quickening, meaning that it moves constantly inside the womb making the mother notice the movement. Mothers usually feel becoming a mother for the first time when life begins to be apparent inside the womb.
Fetal Development – A creamy, cheese-like substance on the skin called vernix caseosa begins to form. Vernix is more apparent in the creases in the body. This protects the baby from cold temperature at birth. The weight of the fetus may now be 283 grams with a length of 25 cm. The 20th week may be the best time to have an ultrasound to look at the gender of the baby.
Week 21
Maternal Changes – Stretch marks may start to appear as the skin starts to stretch to make way for the growing abdomen. Back pain also intensifies because of increased weight of the fetus and placental structures.
Fetal Development – There is no new formation during this stage. The fetus may weigh 369 grams.
Week 22
Maternal Changes – Libido may still be increased during this time because of increased blood flow into the clitoris and the vagina.
Fetal Development – The fetus continues to develop the eyebrows. The average size during this time is 27.5 cm with a weight of 425 grams.
Week 23
Maternal Changes – Swelling of the feet may be apparent because of pressure of the uterus to the major veins on the lower extremities. This may be normal, but swelling in the face and hands may mean more serious indications. Women may also feel slight discomforts from Braxton Hicks contractions or faint contraction of the uterus in preparation for childbirth.
Fetal Development – The lanugo usually darkens. The weight increases to 1 pound.
Week 24
Maternal Changes – The fundus of the uterus usually is in line just above the navel with increasing difficulty of breathing. During the second trimester, there may be lesser frequency of urination than the first trimester because the uterus usually ascends to the pelvic and abdominal cavity.
Fetal Development – Brown fat still continues to be deposited under the skin. The weight of the fetus may be 596 grams or 1.5 pounds. The fetus also grows to up to 12 inches in length.
Week 25
Maternal Changes – This is the beginning of the third trimester. At this point there is increased weight gaining of up to 1 pound per week because of continuous growth of the fetus.
Fetal Development – The bones still continue the hardening process or ossification. The fetus may weigh slightly heavier of 709 grams.
Week 26
Maternal Changes – Sleeping may be especially difficult for women because of the compression of the vena cava. Pregnant women are advised to sleep on their left side to prevent dizziness and hypotension as a result of compressing the vena cava.
Fetal Development – The fetus may start to hear the surroundings on the outside world. In this line, listening to music may help stimulate the baby. The fetus may also be able to see light and dark as light may pass through the skin into the uterus.
Week 27
Maternal Changes – The breast can weigh as much as 14 ounces because of engorgement in preparation for lactation. The amniotic fluid will also increase in amount as evidenced by increased weight.
Fetal Development – The skin of the fetus is usually wrinkled due to presence in amniotic fluid all the time. The wrinkles usually disappear days or weeks after birth. The baby may be as heavy as 900 grams.
Week 28
Maternal Changes – Increase prenatal check-ups are required to at least every two weeks. The breast may also start to produce colostrums, essential breast milk for babies that contain antibodies.
Fetal Development – Subcutaneous fats start to be deposited. Descent of testes among boys may also begin. The baby may weigh up to 1 kilogram and grow as large as 35 cm.
Week 29
Maternal Changes – Increasing discomforts on the back, legs and breathing is starting to get intensified. It is essential to get proper exercise, rest, nutrition as well as good posture to prevent musculoskeletal problems such as cramps, and back aches.
Fetal Development – The bone marrow is fully developed to produce the baby’s own red blood cells and other blood components. The kidneys may also produce up to half a liter of urine everyday.
Week 30
Maternal Changes – Same feelings may affect the mother such as back aches and leg pains. Exercise and good posture is a key to reduced symptoms.
Fetal Development – During this time, the fetus may grow up to 1.36 kilograms and may have length of 37.5 cm.
Week 31
Maternal Changes – The rib cage may be sore because of pressure of the growing fetus in the rib cage. The fetus may also fill up the space in the abdominal cavity displacing all organs inside.
Fetal Development – The iris and pupils of the fetus may now react to light. The skin of the fetus is usually pink. It now weighs up to 1.5 kg. The fingernails may also reach up to the end of the fingers or toes.
Week 32
Maternal Changes – Mothers may be especially concerned about labor as pregnancy comes to end. It is important to discuss fears and concerns to other people as well as to the doctor.
Fetal Development – There may be an increased amount of hair in the scalp. The average weight of the fetus may be 1.7 kg with a length of 16 inches.
Week 33
Maternal Changes – Small bumps may be felt on the abdomen while the baby moves inside the uterus.
Fetal Development – The lungs have already formed surfactant, which helps the baby breathe after birth. When a baby will be born during this stage, the chances of survival are higher than earlier weeks because of the presence of lung surfactant.
Week 34
Maternal Changes – There may be more frequent Braxton Hicks contractions, which help women, prepare for birth. There may be breast milk production as the hormones in the placenta stimulate breast milk production.
Fetal Development – The baby may reach 2 kg in weight and 16.8 inches in length. The baby may also urinate more in the amniotic fluid.
Week 35
Maternal Changes – Increase difficulty of breathing is felt during this time. There may be increased urination, but less often than what happens as you reach term.
Fetal Development – The baby may weigh at least 2.15 kg getting ready for birth. The length may reach 18 inches. The organs have been developed during the first trimester, but finishing touches occur during this time. The baby’s brain may also begin to double in size.
Week 36
Maternal Changes – Prenatal check-ups should be increased to once a week in order to prepare for childbirth. The mother may be relieved of difficulty of breathing as the fetus descends down the pelvis. However, increased urinary frequency is more intense as the fetus pushes more on the bladder.
Fetal Development – The baby may assume a head down position compatible for vaginal delivery. During this time, the fetus also descends into the pelvis ready for delivery. The baby may weigh 2.3 kilograms and has a length of 18 inches.
Week 37
Maternal Changes – The pregnant woman is considered to have reached term staring the 37th week of pregnancy. It is important to prepare the things for birth because the fetus is ready for birth anytime.
Fetal Development – The baby practices breathing by inhaling amniotic fluid in the lungs.
Week 38
Maternal Changes – The woman may feel tingling sensations in the vagina and the legs as the baby’s head settles into the pelvis for delivery as pregnancy symptoms week by week during this stage.
Fetal Development – The weight gain for the fetus during this time is one ounce in a day. There is a large growth happening in the fetus during this time.
Week 39
Maternal Changes – One week left and you’re going to give birth. Some women may have given birth at this time and it is considered term and safe. Lightening may be experienced as the fetus descends further into the true pelvis. Expecting others may present symptoms during this week or few hours prior to labor such as:
- Bloody show in the vagina as a result of loss of mucous plug
- Loose stools
- Increase in appetite
- Sudden increase in energy
Fetal Development – There are no developments happening on the fetus during this time because of imminent delivery. The meconium may reach the rectum ready to be released at birth or few hours after birth.
Week 40
Maternal Changes – The mother is now ready to give birth. The actual percentage of women giving birth on their due date is only 4%. Most of women give birth 2 weeks before or two weeks after expected date of delivery.
Fetal Development – Most of babies during this week have assumed a cephalic presentation for vaginal delivery. However, up to 4% may assume different presentations such as breech or shoulder that may need cesarean birth to prevent fetal distress.
These detailed pregnancy symptoms week by week provides knowledge to pregnant women. These pregnancy symptoms week by week should be observed in order to detect any abnormalities in the mother as well as the fetus. The pregnancy symptoms week by week should also be reported to the physician in order to provide managements for the discomforts.