Penile Fracture (Broken Penis) – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Surgery, Pictures
What is Penile Fracture?
Broken Penis is a fracture of the penis where it affects directly the Tunica albuginea. It is a tissue that envelopes and protects the corpora cavernous penis. The tissue Tunica albuginea is mainly involved in the erection of the penis with the help of the Buck’s fascia where deep dorsal vein restrict the blood from leaving the penis and then maintain the erection. Once the penis is traumatized, the tunica albuginea may be ripped off and cause a bleeding or hematoma on the area. This damage may be the reason why the penis will not erect because the tunica albuginea is broken.
Broken Penis Symptoms & Signs
- Rolling Sign – a firm, stiff, and palpable hematoma – the blood seeped out of the cylinder where it is enveloped by the tunica albuginea
- Pain in the penis
- Ecchymosis of the penis
- Audible popping sound
- Eggplant Deformity – the Broken Penis has the appearance of an eggplant where it is swelled, curved like the letter S, bruised, and angled off towards the other side of the penis.
- Extension of the swelling and hematoma to the scrotum, perineum, and suprapubic region
- Potential injury of the urethra – Dysuria, hematuria, urinary retention, blood present at the penile meatus
Broken Penis Causes & Riskfactors
- When a penis is accidentally traumatized or bended laterally more than it has to during an erection may cause pulling of the stiff tissue of tunica albuginea, therefore lacerating the area. In some instances, Broken Penis happens during a sexual intercourse. Intense and aggressive positions and acrobatic activities can give rise to the pulling and damaging of the tissue of the erected penis and flexing it beyond its strength.
- Aggressive masturbation may put the penis into damaging the tunica albuginea
- Taqaandan – a practice that is performed to detect the existence of erection by bending the head part of the penis while the shaft is erected. There will be a click that is felt and heard. It is similar to the cracking of the knuckles and supposed to be painless. This practice has been reported to cause penile fracture or broken penis.
- Gunshot at the genital area – approximately 35% of the genital injuries are caused by gunshot.
- Stab wounds at the genital area
- Penile Amputation – it involves the mutilation of own genitals. It is mostly associated with people who have psychotic disorders.
- Genital Skin Loss – an infection where in involves gangrene of the soft tissues of the genitalia. It is a rare occurrence but Fournier gangrene makes up the 75% of the cases of genital skin loss.
- Human or Animal Bites on the genital area
- Burns on the genital area
Broken Penis Diagnosis
The Broken penis is usually first seen and diagnosed by taking the health history of the patient, performing the physical examinations. Assessment of the Broken Penis by the health care provider should find the clinical manifestations before diagnosing Broken Penis. In some cases, to detect if there’s a presence of urethral injury in the Broken Penis, imaging studies are done such as
- Cavernosography – a routine specific radiographic visualization of the corpus cavernosum of the Broken Penis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imagery (MRI)
- Urethrographic Studies – this is to confirm or rule out the damage of the urethra and the extension of the trauma.
Broken Penis Treatment
a. Non-invasive medical management
1. Stabilization and Adequate fluids – to replace the blood loss to hematomas
2. The Broken Penis should be given proper compression, penis splints and bandages to avoid unnecessary painful erection of the Broken Penis and further damage the corpus cavernosum.
3. Cold compress – this is to relieve the Broken Penis from pain and hematoma
4. Administration of prescribed medication for the Broken Penis
- Antibiotics are given to avoid the development of infection on the Broken penis
- Estrogens that inhibits the erection the broken penis
- Pain killers are also given to relieve the patient from the pain
- Anticoagulants and thrombolytic drugs to avoid formation to much blood clot that may develop but should be use with proper caution to avoid uncontrolled bleeding.
5. Proper and Sterile Wound Care by cleaning the broken penis of dirt, debris, dead cells and wrapping with sterile gauze that is done every day (or as ordered by the doctor).
b. Invasive Surgical Management
No matter how small or big the trauma has inflicted the penis, surgical restoration of the penis is done to correct the damage done to the tunica albuginea, avoid the complications, erectile dysfunction, and urethral damage. Records show that 92% of the surgeries done had great results. There are three various types of incisions that are done to restore the broken penis:
1. Incision of the affected area to visualize the extension of the defect. It also provides examination of the nerve bundles that are affected in the broken penis.
2. Inguinal – scrotal incision is giving a great view of the broken penis’ root, base, and rear portion.
3. Circumferential – degloving incision is the one that is usually suggested by health care providers because it gives excellent cosmetic outcomes. This is the incision that provides the surgeon the entire exposure of the bilateral corpora cavernosa.
In some cases like penetrating trauma or presence of gangrene in the broken penis, the surgery should include these management:
- The necrotic and gangrene tissue should be incised and debrided.
- Intensive sterile cleaning of the area with antibiotic solution, creams, and Povidine.
- Skin graft is done if the affected area is large and needed to be covered.
Prevention
Erection of the penis is inevitable because it is the penis’ nature to erect when stimulated sexually. One solution is to avoid the position that may cause too much bending of the penis. Also, broken penis occurs when it is banged against the partner’s pubic bone or any hard surfaces.
Pictures
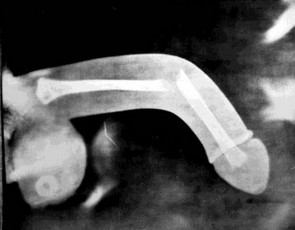
Picture 1 – Diagramatic representation of broken penis (Truely, bone is absent in penis)
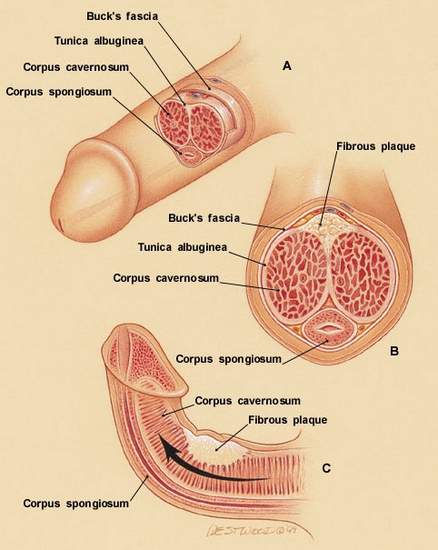
Picture 2 – Real anatomy inside penis
Image Source – peyronies-disease-help.com



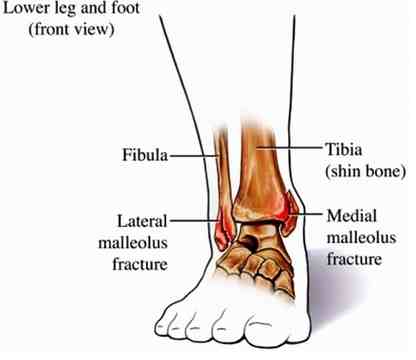 Picture 1 – Pic of broken ankle anatomy
Picture 1 – Pic of broken ankle anatomy