Perioral Dermatitis
What is Perioral Dermatitis?
Perioral dermatitis is a skin condition mostly affecting women and children. This is an inflammatory condition characterized by small pustules and papules that assume a perioral distribution (around the mouth).
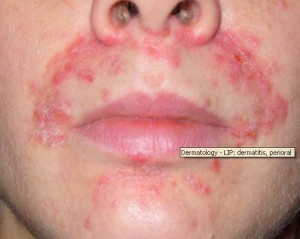
Small Lesions Around the Mouth that Characterize Perioral Dermatitis
This condition sparks and interest among a few because this is a newly emerged disease. Considered to be a disease of the modern era, cases of perioral dermatitis have been recorded just in the recent years of the 50s and 60s. Interestingly, this is the same era when fluoride toothpastes and corticosteroids are used.
Where does the Lesions Emerge?
Aside from the area surrounding the mouth, perioral dermatitis lesions are also seen to affect other parts of the body. Lesions can also be seen around the eye (perioccular) and nostrils (nasolabial folds). Because lesions are not only contained around the mouth, it is now more correctly termed as periorificial dermatitis (peri-around, orifice-opening).
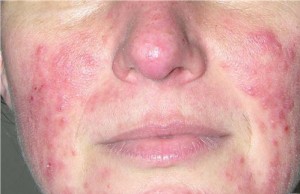
Lesions affecting the rest of the face
Who are the Ones Most Affected?
- Children 6 months to 16 years old
- Women 17-45 years old
Perioral Dermatitis in Children
There are lesser incidences of perioral dermatitis in children. This condition is seen more common in adults than in people of younger ages. But nonetheless, there are still reported cases of perioral dermatitis among children. This condition affects children as young as 6 months to 16 or 18 years of age, and the condition can last up to 8 months.
Symptoms & signs in children
- Papules, pustules or even vesicles appearing around the mouth
- Same eruptions can also occur periorbitally (around the eyes) or perinasally (around the nose)
- Eruptions are accompanied by pruritus
- Eczematous in some cases
- 70% of lesions are perioral
- 43% occurs around the nose
- 25% occurs around the eyes
Causes in children
The exact cause of perioral dermatitis remains unknown, but steroid (whether topical or inhaled) is strongly related to the condition. Almost 72% of periorificial dermatitis in children is correlated with inhaled and topical corticosteroids. The remaining is also attributed to the use of:
- Cosmetic agents
- Fluorinated toothpastes
- Topical fluorinated corticosteroids
- Other irritants or chemical agents.
Perioral Dermatitis in Adults
Symptoms in adults
- Emergence of small papules, pustules or vesicles around the mouth, nose or eyes
- Erythema or redness in the areas of the lesions
- Drying or scaling of the skin on the affected area
- Itching or pruritus
- Burning or stinging sensation (may occur after or during brushing)
- Lesions forming a complete circle around the mouth except at the vermillion border
Causes in adults
Corticosteroid Use
Perioral dermatitis is primarily attributed to corticosteroid use. Certain studies reveal that 71 out of 73 cases of perioral dermatitis have corticosteroid use. In children almost 72% used topical corticosteroids before the emergence of the condition. The exact mechanism why topical corticosteroids cause such condition is still unknown. But experts speculate that topical corticosteroids reduce the protective skin layer and also decrease the size of skin cells (keratinocytes).
Indirect use of corticosteroids is also seen to cause or worsen perioral dermatitis; this is commonly seen in children who use inhaled corticosteroids to treat asthma. Long term use of these corticosteroid inhalers is also seen to have a relation with perioral dermatitis, even if it is not in direct contact with the skin.
Fluorinated Toothpastes/Creams
Another factor seen to cause perioral dermatitis is the use of fluorinated toothpastes, or other fluorine containing compounds. In a study conducted to 65 patients with perioral dermatitis, it was found that almost all of them used fluoride toothpastes. Replacing the toothpastes with non-fluoride relieved the patients of their symptoms.
Microorganisms
In certain cases, particular microbial specie is attributed to perioral dermatitis. Although studies are not yet conclusive, certain cases were seen to be related to the emergence of this condition. Microorganisms seen to cause perioral dermatitis include:
- Fusiform Bacteria
- Dermodexfolliculorum
- Microscopic mites
Certain expert say that the “immune suppressing” effect of corticosteroids may have contributed to the proliferation of such microorganisms. This then leads to perioral dermatitis.
Use of Cosmetics, and other Facial Products
According to certain studies, the use of cosmetics and other facial products can also cause perioral dermatitis. Female patients using night creams, cosmetics, moisturizers and foundation predisposes them to developing perioral dermatitis by 13-fold (according to a clinical trial). Though the exact ingredient that causes this reaction is unknown, patients with perioral dermatitis are advised to discontinue the use of the offending product.
Treatment of Perioral Dermatitis
Discontinuation of Topical Corticosteroids, Fluoride Containing Compounds, and Facial Products
Patients who have a history of topical corticosteroid use, fluoride containing compounds and other facial products are advised to discontinue the offending agents immediately. This would improve the patient’s condition and prevent further occurrence of the lesions.
Discontinuation of corticosteroid use can cause a short term flare of perioral dermatitis. To manage this, following interventions can be done:
- Replacement with a less potent cream such as 1% Hydrocotisone or desonide cream
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors
- 1% Pimecrolimus to reduce the flares
- Replacement of corticosteroids with Intramuscular injections
Oral antibiotics
Oral doses of Tetracycline 200-250 mg two times a day is highly effective in treating perioral dermatitis. Tetracycline treatment is usually given to adults or patients older than 12 years old. This is because the medication can cause enamel staining in children of a younger age.
For children, 250 mg or erythromycin twice or thrice daily is seen to relieve the lesions and other symptoms of perioral dermatitis.
Minocycline and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day is also effective. For minocycline and doxycycline treatment should be as follows:
- Full strength dose to last for 3-4 weeks (or until lesions are lessened)
- Half strength dose to last for an additional 2-4 weeks until the rash has resolved
- Topical Antibiotics
Application of topical antibiotics is seen to hasten the reduction of perioral dermatitis symptoms. Topical antibiotics such as the following can effectively treat perioral dermatitis
- 1% metronidazole applied two times a day
- 2% erythromycin ointment
- Clindamycin gel
Diet for Perioral Dermatitis
Diet Rich In Vitamins A, E and B12
These vitamins promote a healthy skin. Vitamin A helps in regeneration new skin cells, while Vitamin E helps reduce inflammation and protects your skin cells from further damage. Vitamin B12, on the other hand strengthens the skin’s protective barrier preventing further damage and irritation.
Failsafe Diet
The failsafe regimen stands for a diet free of additives, low in salicylates, amines and artificial ingredients. Such compounds can worsen or start an eruption, following this diet for at least 2 to four weeks can help lessen the lesions.
Probiotics and Vitamin C
Probiotics and Vitamin C share one action, and that is to boost the immune system in fighting infections and controlling inflammation. Since perioral dermatitis can be worsened by a secondary infection, preventing such would hasten your recovery.
Is Perioral Dermatitis Contagious?
Perioral dermatitis is not a contagious disease. Contact with a person with perioral dermatitis doesn’t mean you would also acquire the same condition. Perioral dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition; the primary cause of this is a person’s reaction to an offending agent. The reaction is limited only to the person affected, the same agent that causes this cannot be spread to other people, and it may or may not cause the same reaction.
Perioral Dermatitis Pictures
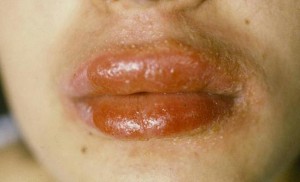
Perioral Dermatitis with Erythema and Swelling of the Lips
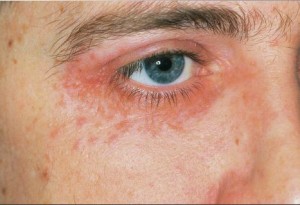
Perioccular Lesions that May Spread from Perioral Dermatitis