Sacroiliac Joint Pain – Treatment, Exercises, Symptoms, Relief
What is Sacroiliac Joint Pain?
Sacroiliac joint pain is basically the unpleasant sensation felt on the lower back reaching up to buttocks and thighs. This is also termed as sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
SI joint pain does not happen in an abrupt manner, it takes years to develop. Throughout the years the muscles lose their balance; this is referred as postural imbalance.si joint pain exercise is very essential to get rid of this Sacroiliac joint pain.
Sacroiliac Joint
Sacroiliac joint is the intersection made by the iliac bones with the sacrum; SI joints are connected by strong intrinsic and extrinsic ligaments. The sacrum supports the spine which is also supported by the iliac bones on each side. There are 2 SI joints, one on the left and the other to the right, usually they are the same in size but varies from person to person.
SI joints work together as a unit and is called bicondylar joints. Bicondylar joints are two surfaces that move correlatively together. There are two kinds of cartilage that cover SI joints: hyaline cartilage covers the sacral surface while fibrocartilage covers the ilial surface.
As a person age, the characteristics of SI joint change. In the early years, the joint’s surfaces are flat and planar, but as a person starts to walk, the surfaces develop angular orientations and lose the flat or planar appearance. An elevated ridge is also developed along the ilial surface while sacral surface develops a depression. With this anatomical design, sacroiliac joints’ stability increase making any dislocations very rare.
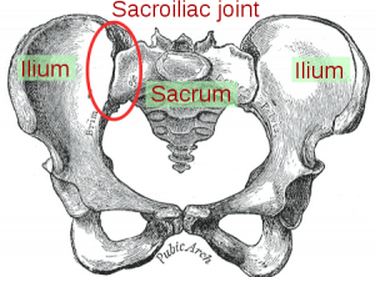
Sacroiliac Joint & its associated anatomical structures
Causes & Risk factors
Sacroiliac join dysfunction refers to hyper or hypo mobility of the joints. It’s either the joints are very mobile and it may be ‘locked’ because of stagnation. This can lead to problems with the ligaments and other surrounding structures. This in turn will result to pain and other associated symptoms.
Causes of sacroiliac pain are divided into 4 categories:
Traumatic
Injuries to the SI joints are caused by sudden collision which shocks the joints. This kind of injury affects the ligaments which supports the joints. An example of this would be landing on the buttocks.
Biomechanical
Biomechanical injuries are caused by increased activity and can be associated with occupation or sports. Most common injuries are:
- Leg length incongruity
- Overpronation
- Twisted pelvis
- Muscle disparity
Hormonal
Hormonal changes throughout the life of a woman pose different kinds of discomfort. During pregnancy, the ligaments that support the joint increase in laxity in preparation for giving birth. Increase in weight plus the increase laxity of the ligaments puts extra strain to the spine causing pain.
Inflammatory joint disease
Inflammatory conditions such as Annkylosing spondylitis give rise to sacroiliac joint pain.
Risk factors that increase the possibility of SI joint pain:
- Poor posture
- Frail muscles
- Twisting the back
- Inappropriate way of lifting
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
Symptoms
The main symptom is a sharp, excruciating pain in the lower back, usually just on side. This is mostly felt in the groin extends down the back of the thighs and sometimes can reach down to the knees. Stiffness on the spine is also observed together with lower back pain. Sacroiliac joint pain is increased in long period of sitting but is frequently alleviated by walking and/or standing.
Diagnosis
Typically, the first step to the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction is through history and physical examination. This determines if there are underlying disorders that might be the cause of patient’s pain. This can also differentiate pain from SI joints, spine or hips. There are various physical examinations that can be performed by the doctor
Patrick’s/Faber’s Test
This is performed by bending the patient’s leg and putting the foot of the assessed leg to the opposite knee. Apply pressure on the superior aspect of assessed knee joint lowering the leg to abduction. The test is positive if pain is noted at the hip or sacral joint, or if the leg can not be paralleled to the opposite leg.
Gaenslen’s Test
This is performed by flexing the hip joint on one side and extending the opposite hip joint. This test can also be done by placing the patient in a lateral recumbent position. The patient lies on his/her affected side and bends the uninvolved hip up to the chest. The involved hip is extended while pelvis is maintained stable. The test is positive if pain is noted while the test is on going.
Thigh Thrust
This is performed while the patient lied supine with one hip bended to a right angle or 90 degrees. The examiner on the same side of the flexed led applies either a quick thrust or provide a steadily increasing pressure through the line of femur. The test is positive if, again, pain is noted while the procedure is performed.
After physical examinations are done, diagnostic testing is also done to confirm the presence of sacroiliac joint dysfunction such as:
- X-ray of the pelvis of back
- CT scan
- MRI
- Biopsy – sample tissue is acquired for testing
- Joint injections – a drug is injected that will block the nerve impulse into the joint; this will determine if the pain starts from the joint.
Management
Most patients can be relieved by physical therapy and if necessary, pharmacologic management.
Exercises (Yoga)
Yoga is a form of complementary and alternative medicine. It is defined as “joining or integrating of all aspects of the individual—body with mind and mind with soul—to achieve a happy, balanced and useful life.” And the ultimate goal of yoga is freedom.
In yoga, incorporation of posture, focused on a specific part of the body, breathing techniques to unite body with the mind and mind to the soul.
There are various types of poses and these are kriyas(actions), mudras (seals), bandhas (locks). Kriya focuses to move energy along the spine; mudra is a gesture to hold energy or concentrate awareness; and bandha utilizes method of holding muscular contractions to focus consciousness.
Yoga helps
- Improve sense of well being
- Reduction of stress
- Decrease heart rate and blood pressure
- Increase lung capacity
- Relaxation of muscles
- Alleviate anxiety and depression
- Improve body flexibility
Back care
To prevent sacroiliac joint pain, it is advisable to prevent stress on the back are by using proper body mechanics in lifting, bending and avoid twisting from the waist.
Pharmacological management
Doctors prescribe medications mainly to alleviate the pain experienced by patients
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Aspirin
- Ibuprofen
- Pain reliever – Tylenol or Acetaminophen
- Steroid injections in the joint