Degenerative Arthritis – Treatment, Symptoms, Causes, Types
What is Degenerative Arthritis?
Degenerative arthritis is a medical condition involving the wearing or degeneration of the cartilage in the joints leading to contact between the two bones. Degenerative arthritis is also termed as osteoarthritis. The cartilage in the joints is the one responsible for the motion of the joint as well as limiting the friction and tension in between the bones in the joints.
In degenerative arthritis, the cartilage is damaged leading to the increased in the friction between the bones. Degenerative arthritis is most commonly seen in weight bearing joints in the body such as the neck, knees and hips, but it can also occur in other joints. The damage in the joint also causes certain changes in the joint capsule as a result of inflammatory response and healing.
The initial response of the joints to damage is the formation of osteophytes in the damaged cartilage. Because of this, there is further narrowing in the joint space. The osteophytes result in the growth of subchondral cysts in the cartilage.
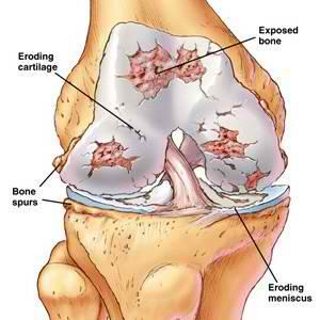
Degenerative Arthritis Image
Image source: health-reply.com
Symptoms of Degenerative Arthritis
Symptoms of degenerative arthritis include:
- Joint pain – The constant friction in the bones in the joint causes inflammatory response on the area causing pain. Pain is characterized as burning and sharp on the joint area, including the muscles and the joints. Cold temperatures usually aggravate the pain. The pain is relieved by gentle motions, but becomes severe with high impact use.
- Stiffness of joints – The other structures such as the muscles, ligaments and tendons in the area are also affected leading to limited motion of the joint. The cartilage that normally allows for smooth motion of the joints is damaged that causes stiffness in the area.
- Swelling of the joint – The joint also appears swollen because of underlying inflammatory process in the area.
- Crepitus – When moving the joint, a characteristic crackling sound is heard because of contact between the bones in the joint.
- Heberden’s nodes – Heberden’s nodes are bony enlargements on the distal interphalangeal joint. These appear because of the growth of subchondral cysts in the joints. These are often not painful.
- Bouchard’s nodes – These are similar to Bouchard’s nodes only that they occur on the proximal interphalangeal joints.
- Joint effusion – The joints may also develop collection of water or fluid as a result of accumulation of synovial fluid in the area.
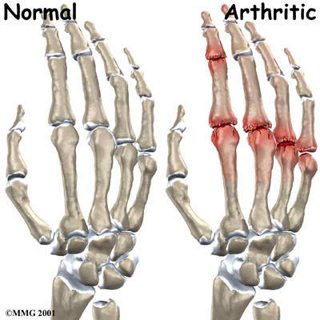
Swelling of the joints
Degenerative Arthritis at Various Places
Degenerative arthritis is most commonly located at weight bearing joints, but it can also occur in all joints in the body. The most common locations include:
Degenerative Arthritis of the Spine
The spine is a common site of degeneration because of bearing the weight of the back and the head. The spine can also be affected by trauma and various inflammatory conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis leading to degenerative arthritis.
Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
The knee is also a common location of the condition especially among obese patients because of increased tension in the area as the knees bear the weight of the body.
Degenerative Arthritis of the Neck
The neck or cervical spine carries the weight of the cranium and its content. It also has several range of motion, which increases the stress in the cervical joints.
Types of Degenerative Arthritis
Primary
Primary degenerative arthritis is a type of joint disorder that is caused by the actual destruction of the joint caused genetic factors. Primary osteoarthritis causes the water content of the cartilage to decrease. The loss of the fluid is associated with aging. The absence of protective fluid or proteoglycan causes the cartilage to become susceptible to damage. Primary osteoarthritis is classified into nodal osteoarthritis and erosive osteoarthritis. Nodal osteoarthritis involves the formation of nodes in the joints, while erosive type involves the progressive destruction of the joint. Erosive from tends to be more severe, but less common than nodal osteoarthritis.
Secondary Osteoarthritis
Secondary osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that results from the degeneration of the joints as a result of underlying conditions that hastens the degeneration of the weight bearing joints.
Causes of Degenerative Arthritis
- Degenerative arthritis is caused by certain factors. Primary and secondary osteoarthritis have different causative factors. The main cause of primary osteoarthritis is genetics. Aging is an aggravating factor because of the normal degeneration of the joint. Secondary osteoarthritis is caused by various factors such as:
- Obesity – Obesity is one of the most common causes of secondary arthritis because of increased tension on the cartilage on the weight bearing joints.
- Congenital disorders – Congenital disorders of the joints involve the presence of defects on the area since birth leading to increased risk for developing degenerative arthritis.
- Inflammatory disorders – Inflammatory disorders such as Lyme disease and Perthe’s disease increases the tendency to develop similar inflammatory condition in the joint.
- Metabolic disorders – Disease such as diabetes and Wilson’s disease also leads to increased degradation of the joints.
- Trauma – Trauma to the joints or ligaments also leads to tearing and injury to the area.
Treatment of Degenerative Arthritis
Various treatments for degenerative arthritis include:
- Weight Loss – Losing weight is an important management for osteoarthritis to prevent further stress and tension in the joints.
- Exercise – Exercise is also essential for patients with osteoarthritis. Stretching exercises are more beneficial because it strengthens the muscles and structures around the joints thereby providing more support.
- Administration of Anti-inflammatory medications – Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen relieve inflammation and pain. Aspirin may also be used, but it can cause adverse reactions such as gastric irritation and bleeding on the joints. Newer medications such as celecoxib can prevent these effects. Cymbalta, an antidepressant drug is also effective in reducing inflammation and pain.
- Apply warm compress – Warm compress may be placed for 15 minutes three times a day to relax the muscles in the area relieving pain.
- Alternative medications – Chondroitin and glucosamine can also be given to patients as food supplements. These substances are a natural component of the synovial fluid. Taking these drugs may help in the synthesis of collagen in the cartilage thereby increasing the integrity of joints.
- Surgery – Surgery becomes the last treatment for degenerative arthritis. This may involve osteomy or the removal of the subchondral cysts and chondroplasty or the repair of the cartilage. Severe cases may require joint replacement by artificial prostheses.