Bleeding After Menopause Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
What is Vaginal Bleeding after Menopause?
Bleeding after Menopause is also called as Post-Menopausal Bleeding (PMB). After reaching your menopausal stage, in rare cases you begin to bleed again. It may be confusing in a woman’s point of view and somehow frightening because of its occurrence.
If a woman already reached her menopausal stage, it is expected that the regular menstruation will stop. But in some cases, bleeding after menopause occurs due to certain underlying factors.
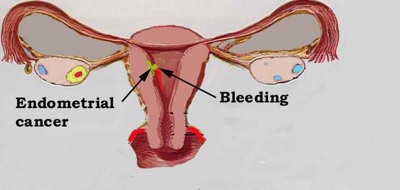
Characteristics of Bleeding after Menopause
- It is considered post-menopausal bleeding if a woman has gone a year with no period and then has it again.
- Post-menopausal bleeding may occur as heavy flow or light flow.
- Women experience this kind of condition almost 20-30% of their population.
- It is common to have post-menopausal bleeding that is due to hormonal shift; the uncommon scene of post-menopausal bleeding is that there may be abnormality in the cells within the uterus.
- Along with these factors, this can be a symptom of hyperplasia of the uterus a minor abnormality in a woman’s body, or of a severe condition; a Uterine cancer.
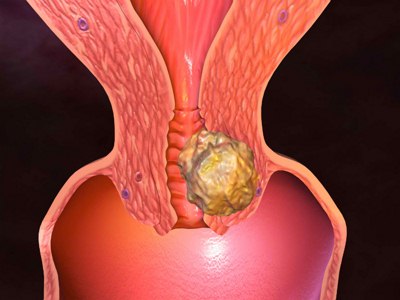
Bleeding after Menopause as a symptom of uterine cancer
All of these conditions are considered highly treatable, but it is the woman who initiates to have this checked to be treated as soon as possible.
In the case that you have bleeding after a long period of time after menopausal, it is best to consult a physician.
Associated Symptoms of Bleeding after Menopause
These are common symptoms you might encounter along with vaginal bleeding after menopause:
- Cramping or Abdominal Pain
- Abdominal, pelvic, or lower back pain that can be severe
- Severe pain on the abdominal, pelvic or lower back part
- Pain in sexual intercourse duration
- Fatigue
Other symptoms that occur along with vaginal bleeding after menopause include:
- Change in bowel movements
- Signs of Constipation
- Irritability and mood swings
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) or fast heart rate as a result of hypovolemia
- Sudden weight gain or loss
- Fever and chills with ill feeling associated with infection
These symptoms indicate presence of further problems in a woman and these should not be ignored. Early detection of underlying causes is important to immediately implement certain treatments.
What Causes Bleeding After Menopause?
Bleeding after menopause can be caused by the following factors:
- Trauma – Trauma can result from sexual intercourse or any foreign body.
- Poor vaginal lubrication – Menopausal women have decrease in vaginal lubrication because of hormonal changes. Because of this, sexual intercourse may be painful or may result in bleeding.
- Hormonal Replacement therapy – Hormonal replacement therapy may cause vaginal bleeding because of fluctuations in the estrogen and progesterone levels.
- Steroids and Anti-coagulants – These can also cause post-menopausal bleeding because of impaired clotting mechanism of the blood.
- Cancer medications -Treatments for cancer, specifically breast cancer may result in post-menopausal bleeding as a side-effect
- Clotting problems as a result of kidney, thyroid or liver disease – These conditions often lead to bleeding because of impaired synthesis of clotting factors.
- Infections – Infections in the reproductive tract such as Chlamydia can also cause post-menopausal bleeding.
- Malignancies – Cancer in the reproductive tract also leads to post-menopausal bleeding.
- Nutritional state, diet, exercise and stress
- Endometriosis – Endometriosis is an excessive proliferation of the lining of the uterus leading to dysfunctional bleeding.
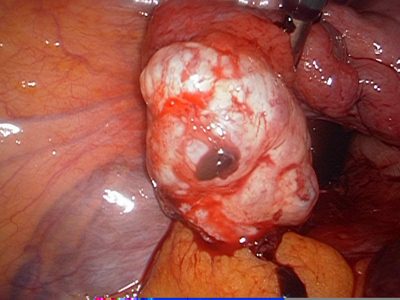
Endometriosis as a cause of bleeding after menopause
How to Diagnose Bleeding After Menopause?
If you have a bruise or notice to bleed so easily, consult a physician because this may mean a bleeding disorder.
Physicians usually diagnose post-menopausal bleeding based on the following tests:
Complete Blood Count
This is done to check the RBC and platelet component of the blood. Low platelets tend to cause bleeding because of reduced platelet aggregation (a step in the clotting process). The RBC, hemoglobin and hematocrit level are also checked to determine extent of bleeding because it may cause anemia.
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT), prothrombin time (PT) and bleeding time determination
These are also checked to evaluate the clotting mechanism in the body. An elevated result may cause bleeding in all areas in the body, including vaginal bleeding.
Thyroid evaluation
Thyroid hormones are also checked because a decrease in thyroid hormones leads to vaginal bleeding.
Pap smear
Pap smear is done to detect cervical cancer.
Pelvic Exam
This is usually done by gynecologist to examine the pelvic organs. Also there are more specific tests that may detect what causes vaginal bleeding after menopause. These include:
- Transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS) – This kind of test can look closely at the organs in the pelvic area. PMB ultrasound is able to show the lining and thickness of the womb. Thus, this can show whether the patient has chances of getting cancer or not.
- Pipelle test – This test is performed along with the TVUS to examine the endometrial cells.
- Out-patient hysteroscopy. If the TVUS and the pipelle test have limited results, the hysteroscopy can be done as an out-patient basis. This test uses a thin scope inserted through the cervix and into the uterus to visualize the area.
- Biopsy. It is a test that involves getting a small sample of the endometrial lining for histologic analysis. This could also be carried out as an out-patient basis.
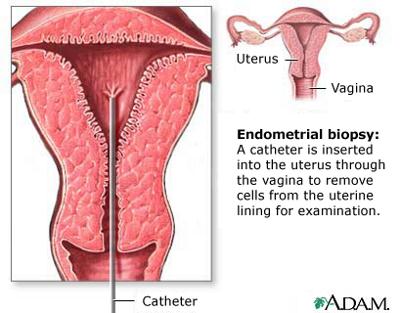
Endometrial Biopsy to determine the cause of bledding after menopause
How to Treat Bleeding After Menopause?
There are different kinds of treatment for vaginal bleeding after menopausal, but it is most recommended to see your doctor first for accurate treatment and diagnosis. Managements applied to manage vaginal bleeding problems include:
Dilatation and Curettage (D&C)
This procedure is done under general anesthesia. It involves scraping the uterine lining to remove dysfunctional cells that lead to dysfunctional bleeding.
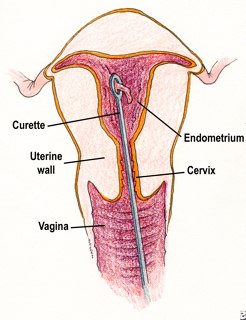
Dilatation and Curettage to treat bleeding after menopause
Platelet transfusion
When platelet counts are low, platelet transfusion is started immediately to prevent profuse bleeding.
Anti-fibrinolyitc therapy
Medications such as Tranexamic acid is given to prevent dissolution of fibrin clots that leads to bleeding. However, anti-fibrinolytic therapy should be carefully used in patients with history of stoke because it promotes blood clots that may be a reason for cerebrovascular accidents.
Remedies for PMB
- Avoid using tampons that can irritate the lining of the vagina. Use pads instead.
- Make sure to change pads every two hours whether it is not soaked. Presence of old blood around the vagina may cause bacterial growth and may lead to sepsis.
- Avoid using anti-coagulants and aspirins to prevent bleeding as a side-effect.
Complications of Bleeding After Menopause
Post-menopausal bleeding needs prompt consultation from a doctor. The post-menopausal bleeding or PMB may be a sign that you have certain conditions that should be attended by health professionals. Complications of such could lead to more severe cases such as:
- Sepsis – Prolonged bleeding encourages bacterial growth that may spread to the blood and other areas of the body.
- Hypovolemia – Blood volume depletion may also result from prolonged bleeding.
- Shock – This may be due to septic shock or hypovolemic shock as manifested by severe hypotension and circulatory collapse.
The presence of vaginal bleeding after menopause should warrant the individual to seek medical attention because complications are often life-threatening. Minor forms of vaginal bleeding such as in the case of trauma, medication side-effects and hormone replacement therapy should still be evaluated to detect any serious underlying condition.