Corneal Ulcer – Treatment, Pictures, Symptoms and Causes
Corneal Ulcer is the deterioration of the external zone of the cornea. Corneal Ulcer is also known as Ulcerative keratitis or Eyesore. This is an inflammatory and infectious condition of the eye, which involves damage of one the layers of the cornea. This is usually seen in people living in tropical countries especially those involve in farming.
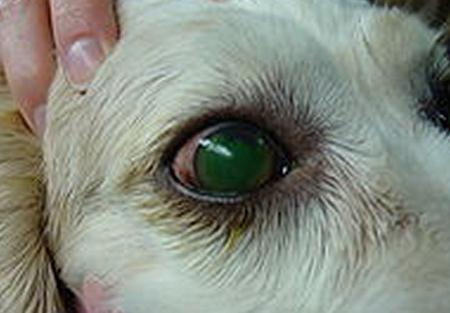
Corneal Ulcer in Dogs
The incidence of corneal ulcer among dogs normally happens when they pat or scratch their paws on their eye. Whenever it is scraped, the cornea becomes inflamed and become hazy. But this usually goes away without intervention.
Picture 1 – Corneal Ulcer in Dogs
Corneal Ulcer Signs & Symptoms
This disorder usually present likes symptoms of infection. Signs and symptoms include:
- Bloodshot eyes
- Intense eye pain
- Lacrimation or tearing
- Clouded and frosty vision
- A disturbing sensation that seems like there is an object inside the eye
- Cannot look directly at bright lights due to intense pain
- Watery eyes
- Tingling sensation
- Dense drainage from the affected eye
- Inflamed eyelids
- Ball-shaped stain in the cornea, which is discernible even with the unaided eye
Corneal Ulcer Causes
The most frequent and usual cause of this disorder is infections by bacteria, parasites, virus or fungi. Others are caused by trauma, disorders of the eye, chemical contact, and some physical agents.
Bacterial causes. This is common among people who regularly use contact lenses either for aesthetic purposes or ophthalmologic purposes.
Viral causes. Virus is also one of the usual causes of this disorder. The most common virus causing this disorder is the herpes simplex virus. This virus can cause injury to the outer parts and on the most immersed part of the surface of the eye sometimes.
Fungal causes. Infections cause by fungi also results in corneal ulcer. This occurs due to inappropriate use of contact lenses and too much usage of steroidal eye drops. Fusarium is usually correlated with the outbreak of fungal keratitis seen among those who wear contact lens.
Parasitic causes. Parasites can also cause corneal ulcer. This is usually caused by the parasite acanthamoeba, which invade the eye through contact lens use. They are normally found in non-flowing forms of water like in the bath tubs, pools and water tap.
Other causes.
- Trauma to the eye can also result in corneal ulcer. This can either be due to accidental bumping of the eye, which results in scrapes and lacerations of the cornea. This insult allows the invasion of microorganisms into the eye causing infection.
- Eyes that have been dry for some time loses its natural barrier against trauma or infection.
- Chronic allergic reaction that affects the eye
- Accidental chemical spatter in the eye
Corneal Ulcer Diagnosis
Diagnosis for this corneal ulcer is usually made through direct scrutiny of the eye under an instrument to enlarge the contour of the eye. This procedure is known as slit lamp. Fluorescein staining allows better visualization of the cornea and will unveil condition of the cornea.
- Scraping a part of the cornea for examination under a microscope will reveal if bacteria or fungi is present.
- Culturing the corneal sample will also reveal specific microorganism.
- Blood work up is also done to see the presence of any inflammatory disorder.
Corneal Ulcer Treatment
Once the disease is properly diagnosed, specific treatment will be given. Your ophthalmologist will discuss management depending on how grave the disease and its cause.
Medications
1. Antibiotics. Antibiotic therapy is given to kill all microorganisms that can cause bacterial corneal ulcer. This is the immediate line of defense for corneal ulcer. Broad spectrum antimicrobials are mostly prescribed to contain all known pathogens.
- Cefazolin: This antibiotic belongs to the first-generation class of cephalosporin. This drug specifically acts on gram-positive bacteria. It is commonly given in addition to aminoglycosides to attain extensive range of coverage. 50-133 mg/ml solution is usually added for better effect.
- Gentamycin: This is an aminoglycoside antimicrobial agent that is specifically sensitive to gram-negative bacteria. Normally given in conjunction with cefazolin for better coverage.
- Erythromycin: This antibiotic drug is prescribed for treating infections brought by predisposed group of bacteria. This is also given for interrupting infections to the cornea and conjunctiva.
- Ophthalmic Ciprofloxacin: This drug is a bactericidal agent that prevents the production of bacterial DNA thereby stopping the development of the bacteria by preventing the DNA gyrase in predisposed individuals. This is also prescribed to patients infected with microorganisms that have become resistant to other antimicrobials.
2. Cycloplegics. These are agents that cause numbness of the ciliary muscles of the eye. They act to reduce the pain brought about by the twitching of eye muscles.
3. Ophthalmic Scopolamine: This drug works by obstructing the function of the agents that control muscle contraction, which makes the pupil of the eye enlarge, and cause numbness and paralysis of eye adjustment.
4. Antivirals. Antiviral therapy starts with mechanically removing the affected part of the cornea. After the removal, introduction of antiviral topical solutions.
- Vidarabine: This drug acts to intervene with the first stages of the production of viruses. This is given if the patient develops an allergic reaction or cannot tolerate Idoxuridine.
- Idoxuridine: This drug is initially prescribed for infections of the epithelium of the eye. It also deter the generation of herpes simples virus by making false DNA counterpart, which avert the virus from contaminating and impairing the tissues.
5. Antifungals. This line broad coverage antifungal produces the least sensation of pain and damage to cornea.
Natamycin: This antifungal drug is the drug of choice for curing infections cause by fungi in the cornea. This acts by binding the fungal cell membrane to form a convoluted and tangled compound, which changes the capacity of the membrane to allow passage and destroying important contents of the cells, killing the fungi. Therapy lasts for 14-21 days up until the desired result is achieved.
6. Adjunctive Drug Therapy. This therapy is needed to treat other conditions related to corneal ulcer or conditions brought about by the disease.
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs). The action of NSAIDs in corneal ulcer is assumed to be related to the suppression of the enzyme prostaglandin. The production of this agent causes constriction and lessened vascular accessibility, increase in the white blood cells and pressure inside the eye.
- Ibuprofen: This is regularly the drug chosen from this group. This is prescribed for the treatment of pain as long as it is not contraindicated to the patient. It acts by repress the reactions of the body to inflammation and pain by lowering the actions of the cyclooxegenase.
- Analgesics. This agent is mainly given to provide comfort to the patient by reducing pain.
- Acetaminophen: This is prescribed for mild to chronic pain.
Surgery
Corneal transplant only indicated when the disease cannot be treated with medications or if the medicines only worsen the condition.
Self Care
These are simple steps in caring for the eye to avoid or prevent the condition from getting worse.
- Remove contact lenses before going to bed.
- Wash your hands regularly especially before touching the eyes.
- Do not stroke the eye with your fingers.
- Place cold pack over the affected eye.
Corneal Ulcer Healing Time
There are two methods by which corneal ulcer heal, by movement of the epithelial cells around the area followed by division of the cells, or via addition of new blood vessel coming from the conjunctiva. Evident tiny ulcers improve very fast by the first approach. Those ulcers, which are bigger and more profound, recover via the second approach. The white blood cells and fibroblasts helps heal the ulcers. They provide new tissues that completely heal the cornea. Normally, corneal ulcers resolve by the end of the fourth day.
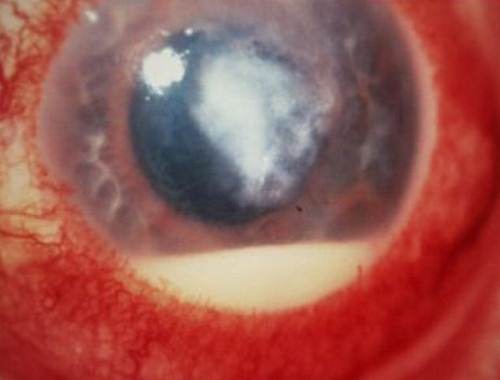
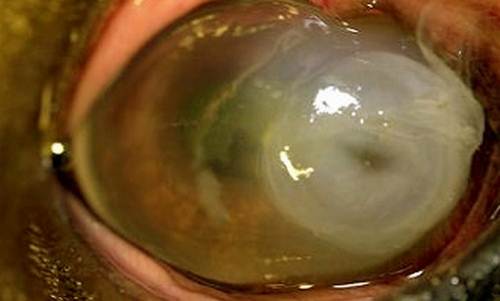
Corneal Ulcer Pictures
Here are the some pictures on corneal ulcer
Picture 2 – Starting stage of corneal Ulcer (easily treated)
Picture 5 – Very Severe stage (observe thinning of cornea). Need Corneal Transplant