Mastoiditis
What is Mastoiditis?
Mastoiditis is a termed used to describe an infection that is located at the person’s mastoid process, which is found on the temporal bone located on the skull just behind the person’s ear. It is often due to otitis media or infection of the person’s middle ear. The infection associated with Mastoiditis is bacterial in nature.
The infection occurs within the mastoid process but some cases have an ear infection which spreads throughout the mucus membrane that surrounds the mastoid itself until it reaches to the bones, which is far graver when reached within this case. It is used to be a leading etiological factor of the death in most children. It often starts with a small infection which progresses into a life-threatening problems or complications.
Mastoiditis Symptoms
Patients with Mastoiditis will manifest the following symptoms associated with the disease condition such as:
- Headache
- Pain in the ear or otherwise known as otalgia
- Irritability
- Tenderness of the ear specially in the mastoid region
- Drainage from the person’s ear which may be brownish in color
- Swelling of the ear
- Erythematous
- Infection of the ear
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Chills
- Anorexia
- Lethargy
- Drooping and bulging of the person’s ear
- Diarrhea or loose bowels
These are the common symptoms associate with this disease condition. The non specific symptoms such as diarrhea, anorexia, irritability or lethargy may be shown in infants.
Mastoiditis Terminology
Acute Mastoiditis
It is a common disease category of Mastoiditis that occurs most often in children. When one neglects it, it may progress to Chronic Mastoiditis. It is a common occurrence before but today with the advancement of medical treatment, it occurs very rare and may be seldom seen. When one has this, the person has a history of infection of the ears. The cardinal sign for this condition is pain. Even after acute form of otitis is treated, the pain will typically subside. However, if the pain worsens, then the person will positively have infection of the mastoid. The inflammatory process will then be manifested which is the dolor, calor, pallor, rubor, function laesa and tumor.
Chronic Mastoiditis
When person will acquire chronic form of Mastoiditis, it usually means that they may or may not have chronic for of otitis media. They have the following symptoms: low grade fever, tenderness and chronic otalgia. This kind of classification of Mastoiditis occurs when the person does not respond well to the treatment or perhaps it recurs often.
Bilateral Mastoiditis
It is a medical term used to describe infection on the mastoid portion which affects both your ears. It may either be in a form of acute or chronic kind. It is due to an untreated kind of infection of the middle ear portion.
Coalescent Mastoiditis
It is a medical term given to persons who have acute form of otomastoiditis. It happens when mucoperiosteal kind of disease that involves the bone. It is the rare kind of infection of the mastoid bony portion or process. When the disease doesn’t respond well to treatment, it may have the possibility to spread to the person’s brain which will then result to disability or worse, to death.
Left Mastoiditis
When a person has this diagnosis, it means to say that the person has an infection of the mastoid portion which is located behind the person’s ear on the left portion. The right ear is unaffected.
Mastoiditis Causes
As mentioned earlier, persons who are afflicted with Mastoiditis have bacterial form of infection. Patients who have the disease condition often were exposed or have a medical history of ear infection, particularly in the middle ear, which may often recur. It affects children. Aside from that, those persons who have weaker immune system may be afflicted with the disease.
Mastoiditis Diagnosis
The physician will conduct examinations to be able to diagnose persons who are suggested to have Mastoiditis. The examination that the patient undergoes includes the following:
- Physical examination
- Medical history examination
- X-ray examination which may or may not be useful but some physician would use it
- Blood test examination
- Ear Gram staining culture examination
- Biopsy
- MRI scan
- CT scan
- Technetium 99 bone scan examination
- Exploratory Surgery for diagnosis
It is suggested that when either of the symptoms above mentioned will be present, there is a need for you to consult a trusted physician as early as possible before the condition becomes worst and treatment will not be any more effective.
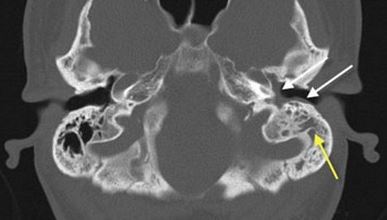
CT scan showing bone infection located at left mastoid process
Mastoiditis Treatment
Depending on the extent of the disease condition, the person with Mastoiditis is at the most treated by either:
- Antibiotics to treat the bacterial infection and which may be done intravenously which is the fastest route to use. Oral antibiotics will be given after the intravenous antibiotic is given.
- Antipyretics to treat fever episodes that are brought about by the inflammatory process or in the presence of fever.
- Myringotomy which may prevent ear infection in the future and Mastoiditis that appears subsequently. It is done to drain the ear fluid found in the middle ear portion.
- Mastoidectomy which is a surgical procedure done especially when the treatment mentioned above is unsuccessful. Here, the mastoid portion is removed to prevent the spreading of the infection to the nearby areas.
Mastoiditis Complications
When undergoing a serious surgical procedure, you must outweigh advantage and disadvantage to consider, for it can result to serious complications such as
- Blood clot
- Brain abscess
- Meningitis
- Hearing loss
- Bell’s palsy
- Osteomyelitis
- Otitis media
- Cellulitis
- The mastoid bone is destroyed
- Vertigo or dizziness
- Facial paralysis
Hence, do not wait for this to occur. Although most of the complications are of rare occurrence, there is a need to seek treatment promptly.
One thing is for sure, is that the complications which are associated with this disease condition are rare. However, the complications will occur if the person does not seek immediate medical care and if the person does not respond well to the treatment provided.