Optic Nerve Hypoplasia – Definition, Treatment, Causes, Symptoms
What is Optic Nerve Hypoplasia?
Optic nerve hypoplasia is a condition involving the underdevelopment of the optic nerves that commonly occurs as a result of congenital optic nerve anomaly. In optic nerve hypoplasia, the optic nerve axons have not developed properly leading to an abnormally small optic disc. The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting the signals of vision from the retina to the brain. The optic nerve usually consists of up to 1.2 million of optic nerve fibers. In optic nerve hypoplasia, there are fewer nerve fibers leading to problems in the vision.
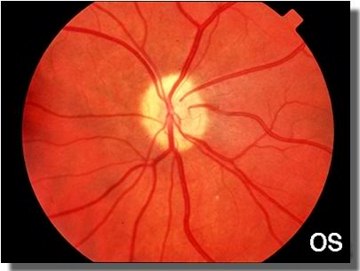
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Image
Image source: njms2.umdnj.edu
Optic nerve hypoplasia is more commonly related to brain malformations, developmental delay as well as endocrine problems or hormone deficiency. Aside from the problems in the optic nerve, there are also problems relating to anomalies in the hypothalamus, maldevelopment of the pituitary gland, absence of septum pellucidum and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Due to these, patients with optic nerve hypoplasia are also prone to hormonal deficiencies and developmental delays.
Optic nerve hypoplasia has become the leading cause of infant blindness in Sweden, overtaking the position from retinopathy of prematurity. Optic nerve hypoplasia may affect all races, but is lesser prevalent in Asian populations.
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Symptoms
Optic nerve hypoplasia causes symptoms in the vision as well as symptoms related to the accompanying problems in the brain. These include:
Vision problems
Children with ONH suffer from strabismus or the inability to align the eye simultaneously or nystagmus or the involuntary eye movements. Vision problems may be bilateral or unilateral. Children with unilateral vision problem have better vision. Vision problems tend to improve during the first few years of the child. Vision problem also do not result in decline or progression.

Strabismus as one of the symptoms of Optic Nerve Hypoplasia
Image source: babble.com
Hypothalamic symptoms
Because of problems in the hypothalamus, children often lead to problems in the regulation of the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is responsible for the regulation of the hormones in the body. Problems in the hypothalamus may lead to poor functioning of the pituitary gland or hypopituitarism. Hypopituitarism is often present in up to 80% of patients with ONH. As a result, there is poor function leading to lack of growth hormone, adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism and diabetes insipidus. Symptoms depend on the hormone affected. These include:
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Short stature
- Hypoglycemia
- Seizures
- Jaundice
- Delayed dentition
- Micropenis in boys
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism may lead to mental retardation when left untreated because of poor metabolism and development of the brain. Hypothyroidism manifests as:
- Cold intolerance
- Water retention
- Rapid weight gaining
- Adrenal Insufficiency
- Precocious puberty because of problems in sex hormones
- Obesity
- Inability to cope with stress because cortisol deficiency
- Diabetes insipidus
- Excessive urination
- Dehydration
- High sodium levels in the body
Other problems involving hypothalamic affectation involve problems in sleep, feeding and regulation of the body temperature. Because of these, children often exhibit overeating and obesity or reduced food intake that may or may not lead to weight loss. Children also suffer from abnormal sleep wake cycle leading to behavioral problems.
Neurologic problems
The presence of malformations in the brain causes developmental delay such as motor delays, which affects up to 75% of cases and communication delay, which affects up to 44% of children.
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Causes
Optic nerve hypoplasia is related to several prenatal and perinatal risk factors. These include:
- Young maternal age – Mothers who are young have been related to the development of optic nerve hypoplasia.
- Primiparity – Infants who are first born usually suffer from the condition.
- Increased number of cesarean delivery among mothers
- Gestational vaginal bleeding
- Preterm labor
- Low maternal weight gain
- Weight loss during pregnancy.
All these factors are associated with the development of the fetus leading to optic nerve hypoplasia.
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ONH involves opthalmoscopic examination that indicates small optic nerve. The DM:DD ratio is also used to ascertain diagnosis. DM refers to Disk to Macula, which is the distance of the center of the disc to the macula. DD refers to the Disc Diameter. When the ratio is greater than 3, there is suspicion of ONH. However, when the ratio is greater than 4, ONH is definite.
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Treatment
Optic nerve hypoplasia has no treatment because of permanent damage of the optic nerve. However,optic nerve hypoplasia treatments are available for the symptomatic relief of patients. These include:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy – The presence of hypopituitarism may require hormone replacement to manage symptoms of hypopituitarism as wells as regain the normal functioning of the body. Hormone replacement may include growth hormone therapy, thyroid hormone replacement, estrogen and testosterone therapy and others. These treatments reverse the effects of hypopituitarism in order for the client to live normally.
- Physical and occupational therapy – These therapies are also needed to help patients achieve optimum functioning and address motor delays. These therapies are started as soon as possible to allow children to minimize functional disabilities.
- Speech therapy – Speech therapy is also beneficial to assist the child in communication as a result of communication delays. Speech therapy may start as early as infancy when the child learns how to talk.
- Melatonin administration – Melatonin is also given to enhance the sleep pattern of children. Melatonin given at night adjusts the circadian rhythm of children that have been affected by hypothalamic dysfunction.
- Eye patching – Patching of the good eye is done to improve the vision of the affected eye in the presence of strabismus. This technique allows the better use of the affected eye. Eye patching is only done in cases where the vision is known to improve in both eyes.
- Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Surgery – Surgery for children involves the alignment of the eyes in children with strabismus. The surgery involves the repair of the muscles that control the eye movement. Eye surgery is done when the child already has developed visual acuity, which is commonly achieved after three years of age. However, the eye surgery only involves correction of the eye deformity and it does not improve the vision.
After treatment, the prognosis of ONH is variable. Patients may have near normal vision and some may have legal blindness. Patients may also suffer from intellectual disabilities, despite treatment.