Spondyloarthropathy – Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Spondyloarthropathy Definition
Spondyloarthropathy is a group of diseases involving the joint in the vertebral column. The presence of inflammation along with the joint disease is known as spondyloarthritis. Generally, spondyloarthropathy involves any joint involvement in the vertebral column that may result from any joint disease.
Spondyloarthropathy Image
Symptoms of Spondyloarthropathy
Swelling of one or more joints especially the sacroilial joint – The primary manifestation of spondyloarthropathy is swelling and inflammation of one or more joints including the spine. The sacroilial joint is most commonly affected. The entheses or the connection of the tendons and ligaments on the bones are also inflamed.
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back and buttocks – The inflammation of the spine commonly leads to pain in the lower back that may radiate to the buttocks. Prolonged inflammation may cause arthritic changes that further leads to stiffness.
- Stiffness in the neck and chest – Being a systemic inflammatory disease, the inflammation may also affect the joints in the neck and chest. The shoulders and the legs may also be affected, leading to generalized stiffness of joints.
- Rigid spine – Over time, the spine may fuse together especially in ankylosing spondylitis. The fusion leads to the complete absence of motion of the joints in the spine.
- Limited range of motion of the trunk – The person may not be able to move the trunk leading to functional disability caused by the affectation of the vertebral column.
- Fever and Fatigue – The person may also experience fever and fatigue as a sign of systemic inflammatory condition.
- Inflammation of the bowels – The bowels also suffer from inflammatory condition, which may manifest as abdominal discomfort and problems in bowel elimination.
- Inflammation of the eyes structures – The eye area may also be affected that can lead to inflammation of the conjunctiva, eye lids and other eye structures. The inflammation is often non-infectious.
Severe cases may also lead to lung and heart problems because of stiffness of the joint in the chest.
Types of Spondyloarthropathy
Seronegative spondyloarthropathy
Seronegative spondyloarthropathy is a group of joint disease that involves the axial skeleton. Being seronegative, the patient does not exhibit the presence of rheumatoid factor in the blood. This means that the pathophysiologic mechanism of the condition is different from rheumatoid arthritis.
There are different types of seronegative spondyloarthropathy including:
- Ankylosing Spondylitis – Ankylosing spondylitis is a systemic, chronic inflammatory disease of the joints in the spine as well as other joints in the body such as the neck, hips, shoulders and the joints in the chest. Ankylosing spondylitis may be mild to severe and may cause fusion of the vertebral column after prolonged inflammation.
- Inflammatory spondyloarthropathy – Inflammatory spondyloarthropathy or reactive arthritis is as non-infectious inflammation of the joints in the body. It is usually preceded by gastrointestinal or genitourinary infection. The inflammation may also affect the eyes, skin, GIT and genitals. Reactive arthritis is usually self-limiting and may follow a course of up to 12 months. The condition is usually mild.
- Psoriatic spondyloarthropathy – Psoriatic spondyloarthropathy is the inflammation of the joints in the spine with resulting inflammation of the skin that leads to rapid formation of skin cells leading to psoriasis or the scaly appearance of the skin.
- Enteropathic spondyloarthropathy – This is a spine and peripheral joint disease, which is associated with the occurrence of inflammatory bowel disease like Ulcerative Colitis and Chron’s disease. Enteropathic spondyloarthropathy is also considered juvenile because it is most common in children and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease. This type rarely leads to joint destruction or deformity.
- Undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy – Undifferentiated type may involve one or more conditions, which do not fall under a specific type of spondyloarthropathy
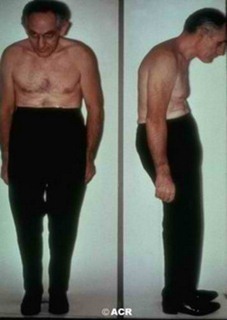
Undifferentiated Spondyloarthropathy Image
Causes of Spondyloarthropathy
The exact cause of spondyloarthropathy is unknown, but certain factors such as genetics and environment has played a role in its development.
Genetics
The presence of HLA-B27 gene was found in majority of patients with spondyloarthropathy. Because of genetics, spondyloarthropathy is considered having familial predisposition. Homozygous individuals are more at risk for developing the disease. Up to 60% of twins also have similar spondyloarthropathy.
Bacterial Infection
Bacteria such as Klebsiella species was found to produce antigenic properties that lead to spondyloarthropathy. Antigens from the bacteria often include arthritogenic properties that may affect the connective tissues and the joints in the vertebral column as the bacteria travels through the blood stream from the gastrointestinal tract. The bacteria initially affect the GIT and produce inflammation in the area.
Diagnosis of Spondyloarthropathy
The diagnosis begins with physical examination and review of the symptoms. Confirmatory diagnosis may include:
X-rays
X-ray of the joints especially the sacroilial joint and the spine usually confirms the diagnosis.
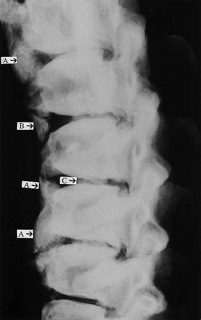
X – ray imaging showing presence of Spondyloarthropathy
Blood tests
Blood tests may also be done to check the presence of HLA B27 gene. However, its presence is not considered confirmatory. The absence of rheumatoid factor also indicates seronegative condition.
Treatment & Diet for Spondyloarthropathy
There is no definite cure for spondyloarthropathies. Treatments usually focus on alleviating pain and other symptoms of the disease. Treatments also aim at preserving joint movement and slow down the disease progression. Treatments include:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is employed to maintain the normal range of motion of joints. It involves strengthening and stretching exercises as well as breathing exercises and maintenance of good posture.
Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually given to relive pain and inflammation. Steroids are rarely administered because it does not improve spinal symptoms. However, it may be used for secondary inflammation of the tendons through injection. Anti-tumor necrosis factors such as adalimumab (Humira), etanercept (Enbrel) and infliximab (Remicade) have been used via intravenous route to slow the progression of ankylosing spondylitis. Other medications for rheumatoid arthritis such as sulfasalazine and methotrexate may also be administered to control the symptoms.
Surgery
Surgical treatments are often not employed, but joint replacements of the hip and shoulders may be done for severe cases that have affected these areas. In enteropathic spondyloarthopathy, colectomy or the surgical removal of the affected colon may be done to reduce inflammation.
Dietary Management
High protein diet is also essential in the management of spondyloarthropathy to hasten the healing process of the joints. However, high levels of purine in the diet should be avoided because purine is metabolized into uric acid that may predispose to the development of gouty arthritis, which may aggravate the condition.