Cartilage Piercing
What is Cartilage Piercing?
Cartilage piercing is the process of creating a hole on the cartilage usually on the ears to make room for jewelries. Cartilage piercing is often placed for aesthetic purposes. Cartilages are present all over the body, but the most common site for piercing is in the ears. Earrings are more commonly used by women, but men who undergo cartilage piercing can also have such.
Piercings on the earlobe, which is commonly seen in women is called earlobe piercing. Piercing on the more tough areas on the ears (such as in the upper part) is termed cartilage piercing. Cartilage piercings require more sophistication in creating than earlobe piercing because of the difference in the toughness of the tissues. Cartilage piercing also takes longer time to heal.

Ear Cartilage Piercing Image
Image source: ehowcdn.com
Does Cartilage Piercing Hurt?
Cartilage piercing usually results to pain because of the inflammatory process involved. Any type of trauma to the skin results to pain. This is due to the inflammatory process that is stimulated by the broken skin and tissues. However, pain experienced following cartilage piercing is minimal and can be tolerated well without the use of analgesic. The pain usually last for 3 days, but it is barely noticeable after the second day.
Types of Cartilage Piercings
Cartilage piercings are vast and involves a lot of types and locations. These include:
Helix Piercings – Helix piercings are piercings placed on the outer edge of the ear and may be placed on the space between the tops and middle of the ear.
Conch Piercing – Conch piercings are piercings placed on the concave portion of the ear located just before the ear canal.
Daith Piercing – Daith piercing is done on the cartilage fold near the ear canal. The creation of daith piercing depends on the availability of space for the ring or bar. Some individuals do not have large cartilage folds on the area making daith piercing difficult.
Industrial Piercing – Industrial piercings are vertical or horizontal piercings inserted on the outer rim of the ears. This involves the placement of two piercings on top and bottom of the ear connected by a long bar in a vertical or angled manner.
Lobe Piercing – Lobe piercings are the most popular ear piercings especially for women.
Orbital Piercing – Orbital piercings are piercings that enter and exit the same part of the ear. This involves the use of an earring going through both piercing holes. Orbital piercings are usually placed on the outer rim of the ear, but may be placed in other locations.
Scaffold Piercing – Scaffold piercing is a popular piercing that usually stands out. This uses two ear piercings that is connected with a barbell. It is commonly placed across the upper portion of the ear in a horizontal or angled approach.
Stretched Lobes – Stretched lobes usually use a tunnel-like piercing placed on the earlobe, which allows stretching of the soft tissue. Stretching is also called gauging of the earlobes. The gauge of the jewelry is gradually increased to allow for maximum stretching of the earlobe.
Rook Piercing – Rook piercing is placed on the highest fold of the ear between the lowest fold (daith piercing) and outer rim of ear.
Snug Piercing – Snug piercings are located on the lower half of the outer rim of the ear.
Tragus Piercing – The tragus is the hard cartilage that sticks out in front of the ear canal. Tragus piercings are placed in this location and is a popular type of cartilage piercing.
Locations of Cartilage Piercings
Cartilage piercings can be placed on various areas of the ear depending on the type of cartilage piercing. These include:
- Auricle or the middle portion of the outer rim. The auricle is the common location for helix piercings and auricle piercings.
- Pinna or the top of the outer rim of the ear. This is also a common site for helix piercings.
- Tragus
- Lower fold of the ear
- Upper fold of the ear
- Earlobes
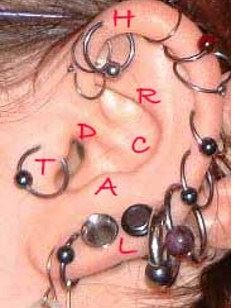
Locations of ear cartilage piercing
Cartilage Piercing Earrings and Jewelry
Earrings used for cartilage piercing can be made from metals, glass, plastic, wood, precious stones and even bone. There are a lot of designs from studs, to loops and danglings. Earrings may also have varied sizes depending on the preference of people and according to the size of their ear. Other people prefer hypoallergenic jewelries because of allergic reactions to plastics and certain materials.
How is Cartilage Piercing Done?
Cartilage piercing has a variety of techniques. It can be done in a clinic and even at home. The procedure of cartilage piercing involves:
- The area is cleaned using an antiseptic such as alcohol.
- Local anesthetics are placed to reduce pain.
- The piercing or gun or needle is used to bore the area.
- A sewing thread may be placed to keep the piercing open until healing or a hypoallergenic earring may be placed.
- Home piercing may also be done by the use of a conventional needle. The pierced area should be cleaned regularly by removing crusts from the healing wound.
Problems and Risk Associated with Cartilage Piercing
Different health risks can be experienced following ear piercing. However, these are commonly minor and can be easily prevented and managed. These include:
Allergic Reaction
Allergic reactions are commonly a result of reactions on the jewelry. Some people are allergic to materials other than metals such as plastics, wood, and bones.
Tearing
Tearing results from accidental perforation of the piercing because of wearing heavy earrings during the healing stage.
Keloid
Keloids can occur when the area is infected, thereby increasing the hypertrophy of cells during healing.
Cartilage Piercing Infection
Infection can also occur as a result of entry of microorganisms in the area.
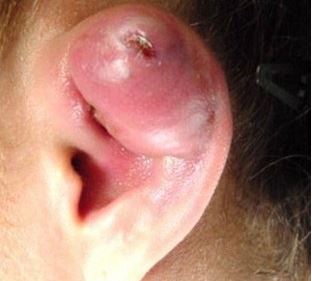
Infection due to unsterile Cartilage Piercing Procedure
Cartilage Piercing Symptoms
Infection of the cartilage piercing manifests with:
- Redness of the area
- Burning Sensation
- Whitish to yellowish discharge
- Swelling
- Causes
- Infection may be caused by a lot of factors such as:
- Using dirty piercing equipment
- Frequent touching of the area with dirty hands
- Poor quality of accessories
- Unsterile procedure during piercing
- Treatment
- Treatment of cartilage infections include:
- Washing the area with a salt solution at least two times a day
- Rubbing ice cubes to reduce swelling and discharges
- Avoiding frequent contact
Cartilage Piercing Healing and Stages
The healing of cartilage piercing follows a certain stage. These are:
Inflammatory phase
The initial stage is the inflammatory stage to allow chemical mediators to heal the wound.
Growth or Proliferative Phase
This phase involves the synthesis of proteins and cells to heal the wound and allow the creation of a fistula or a tunnel of scar tissue. This phase usually lasts for weeks.
Maturation or Remodeling Phase
This phase involves the strengthening of the fistula. After this phase, the piecing is completely healed.
Absence of external and internal factors such as infection and trauma allows the normal and complete healing of the punctured wound.
How to Hide Cartilage Piercing?
Cartilage piercing can be prohibited in some instances in which hiding is the best option especially during the healing stage. When the fistula has not been completely healed, it is not advisable to remove the jewelry because it may lead to closure. Here are several suggestions in order to hide piercings:
- Let your hair cover the piercing.
- During times that the hair should be kept in a ponytail, use a skin-toned band-aid to cover the piercing.
- Substitute large jewelries with small, transparent items.
Cartilage Piercing Prices
The price of cartilage piercing usually differs according to the type and location. The jewelry also has varied prices depending on the materials used. Metals as well as precious stones cost higher than other materials. The average price for cartilage piercing including the jewelry is $50.